
What is Non-Response Bias?
Non-response bias is a type of bias that happens due to differences between those who respond to surveys and those who drop out. The difference between respondents and non-respondents has lots of impact on the objective. It is also called participation bias.
This may happen due to various reasons including some may terminate surveys due to poor survey design and some may drop out on account of asking for confidential info about illegal activity and many more.
For example – A survey asking about video games targeted at people over 50, will likely receive no response. Even the targeted audience is incorrect here.
Why Surveys and Studies?
We live in a world with a large population and vast cultures, religions, perceptions, histories, and whatnot. Everyone is quite different from the other being that we can only try to categorize people but we will fail very badly.
If two people have ‘x’ similar traits even then the possibility of them liking/disliking or agreeing/disagreeing on something is unpredictable. So predicting the market, community or a group of people is next to impossible. What’s the solution then?
Surveys, we take surveys and study them to understand the market or any trend in the world. And that is the reason why “Surveys and Studies” hold a great value in any sector.
Surveys and NRB (Non-Response Bias)
Now the question arises, How can NRB(Non Response Bias) affect the study? Whenever a survey is held, there are some options/choices available for people to choose from. If one does not complete the survey, it creates a report with false data.
Non-Response Bias Mathematical explanation:
Let the number of participants be 4 | => n=4
Let the options be:
-
- Option a
- Option b
- Option c
- Option d
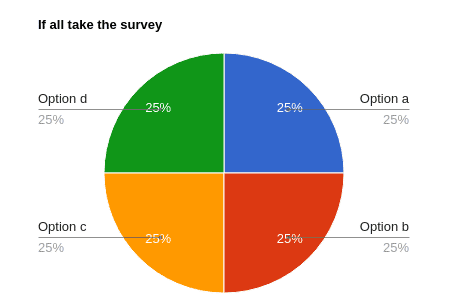
Now if every user select unique option,
Survey Results:
Option a – 25%
Option b – 25%
Option c – 25%
Option d – 25%
Now if one user do not takes the survey,
Survey Results:
Option a – 33.33%
Option b – 33.33%
Option c – 33.33%
Option d – 0%
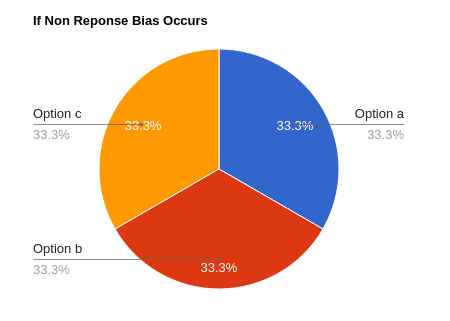
The percentage of these options change significantly if one of the users skips or does not complete the survey.
Who gets affected by the NRB (Non-Response Bias) :
- Health sector: The health sector suffers a lot due to NRB(Non Response Bias) as they get false or inaccurate data. It creates a problem in understanding the problem and the severeness of the issue.
- Research data: When research is going on, it is important to have the right information to solve the issue. We can take in consideration the example of COID-19. Due to incomplete/boreman kind of data, we were not able to understand the scale of issue and we failed in galvanizing the resources required.
- Government Resources: Government resources are really important in any country and it is not possible to use them efficiently until and unless we don’t know the quantity of resources required and what steps can be taken to optimize the approach and resources.
How to avoid NRB (Non-Response Bias) ?
Use close-ended questions. As they are more straightforward with no descriptive response required. Survey platforms like QuestionPro provide a huge set of question libraries which can be very helpful.
Understand your targeted audience. As the wording of questions and whole content may be influential for different audiences.
Provide rewards. Provide rewards to respondents. It can be gift cards etc. For the same, today we have awesome survey software like QuestionPro which can automate the same for you in a single click. You just need to set the criteria and all will be in one go.
Sending reminders to respondents. Some respondents might forget to give a response, so automated reminders might help greatly in this scenario. Platforms like QuestionPro include such awesome features of sending scheduled reminders where you can add scheduled reminders in a single click and that’s it.
Conclusion
Biases may be one of the things that can’t be avoided when carrying out surveys. They can, however, be reduced by making an effort to prevent them from happening.
The first step to do this is by understanding response bias and non-response bias which may be caused by either the researcher or the respondent. Sometimes, these biases may be unintentional, like in the case of a respondent who forgets to respond to a survey.
Authors: Ashish Jangu & Priyansh Datyal







