
Indeed, discovering a chatbot capable of understanding emotional intent or a voice bot’s discerning tone might seem like a sci-fi concept. Still, these technologies are already shaping our reality. Semantic analysis, the engine behind these advancements, dives into the meaning embedded in the text, unraveling emotional nuances and intended messages. It’s the bridge between human expression and machine comprehension.
Semantic analysis techniques involve extracting meaning from text through grammatical analysis and discerning connections between words in context. This process empowers computers to interpret words and entire passages or documents. Word sense disambiguation, a vital aspect, helps determine multiple meanings of words. This proficiency goes beyond comprehension; it drives data analysis, guides customer feedback strategies, shapes customer-centric approaches, automates processes, and deciphers unstructured text.
The implications of the analysis stretch across diverse domains. It’s not just about understanding text; it’s about inferring intent, unraveling emotions, and enabling machines to interpret human communication with remarkable accuracy and depth. From optimizing data-driven strategies to refining automated processes, semantic analysis serves as the backbone, transforming how machines comprehend language and enhancing human-technology interactions.
But:
- What is this technology, and what are the problems that come with it?
- What are the pros and cons, and how does it affect customer relations?
- And how can it be used as part of a plan to improve the customer experience?
Continue reading this blog to learn more about semantic analysis and how it can work with examples.
What is Semantic Analysis?
Semantic analysis is a crucial component of natural language processing (NLP) that concentrates on understanding the meaning, interpretation, and relationships between words, phrases, and sentences in a given context. It goes beyond merely analyzing a sentence’s syntax (structure and grammar) and delves into the intended meaning.
It is a crucial component of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and the inspiration for applications like chatbots, search engines, and text analysis tools using machine learning.
Tools based on semantic analysis can assist businesses in automatically extracting useful information from unstructured data, including emails, support requests, and consumer comments. We’ll go over its operation below.
Advantages of Semantic Analysis
Semantic analysis offers several advantages across various fields and applications:
Improved Understanding of Text:
It helps understand the true meaning of words, phrases, and sentences, leading to a more accurate interpretation of text.
Enhanced Search and Information Retrieval:
Search engines can provide more relevant results by understanding user queries better, considering the context and meaning rather than just keywords.
Better Natural Language Processing (NLP):
Semantic analysis forms the backbone of many NLP tasks, enabling machines to understand and process language more effectively, leading to improved machine translation, sentiment analysis, etc.
Improved Machine Learning Models:
In AI and machine learning, semantic analysis helps in feature extraction, sentiment analysis, and understanding relationships in data, which enhances the performance of models.
Enhanced User Experience:
Chatbots, virtual assistants, and recommendation systems benefit from semantic analysis by providing more accurate and context-aware responses, thus significantly improving user satisfaction.
Personalization and Recommendation Systems:
Semantic analysis allows for a deeper understanding of user preferences, enabling personalized recommendations in e-commerce, content curation, and more.
Semantic analysis significantly improves language understanding, enabling machines to process, analyze, and generate text with greater accuracy and context sensitivity. Indeed, semantic analysis is pivotal, fostering better user experiences and enabling more efficient information retrieval and processing.
How Semantic Analysis Works?
Semantic analysis, a natural language processing method, entails examining the meaning of words and phrases to comprehend the intended purpose of a sentence or paragraph. Additionally, it delves into the contextual understanding and relationships between linguistic elements, enabling a deeper comprehension of textual content.
This is often accomplished by locating and extracting the key ideas and connections found in the text utilizing algorithms and AI approaches.
Semantic analysis employs various methods, but they all aim to comprehend the text’s meaning in a manner comparable to that of a human. This can entail figuring out the text’s primary ideas and themes and their connections.
- One popular semantic analysis method combines machine learning and natural language processing to find the text’s main ideas and connections. This can entail employing a machine learning model trained on a vast body of text to analyze new text and discover its key ideas and relationships.
- Another strategy is to utilize pre-established ontologies and structured databases of concepts and relationships in a particular subject. Semantic analysis algorithms can more quickly find and extract pertinent information from the text by utilizing these ontologies.
The analysis, in general, is a key method for assisting computers in comprehending the meaning of natural language text. It has numerous uses in fields including search engines, information retrieval, and machine translation.
In semantic analysis, lexical semantics is crucial because it enables computers to comprehend the connections between lexical elements (words, phrasal verbs, etc.):
- Hyponymy: It illustrates the connection between a generic phrase and its occurrences. In this context, hyponyms describe instances of the generic term hypernym.
- Homonymy: It can be explained as when two words have the same form or spelling but a completely distinct meaning.
- Polysemy: The Greek term “polysemy” implies “many signs.” It is a phrase or term that has a distinct yet connected meaning. In other words, while polysemy has the same spelling, its purposes are particular yet connected.
- Synonymy: This represents the relationship between two lexical elements with different forms but the same or similar meanings.
- Antonymy: It is the balanced relationship between two lexical elements about an axis throughout their semantic components.
- Meronomy: It is how text and words are put together in a way that makes sense and shows a part or member of something.
Where does Semantic Analysis Work?
Semantic analysis finds applications in various fields, including:
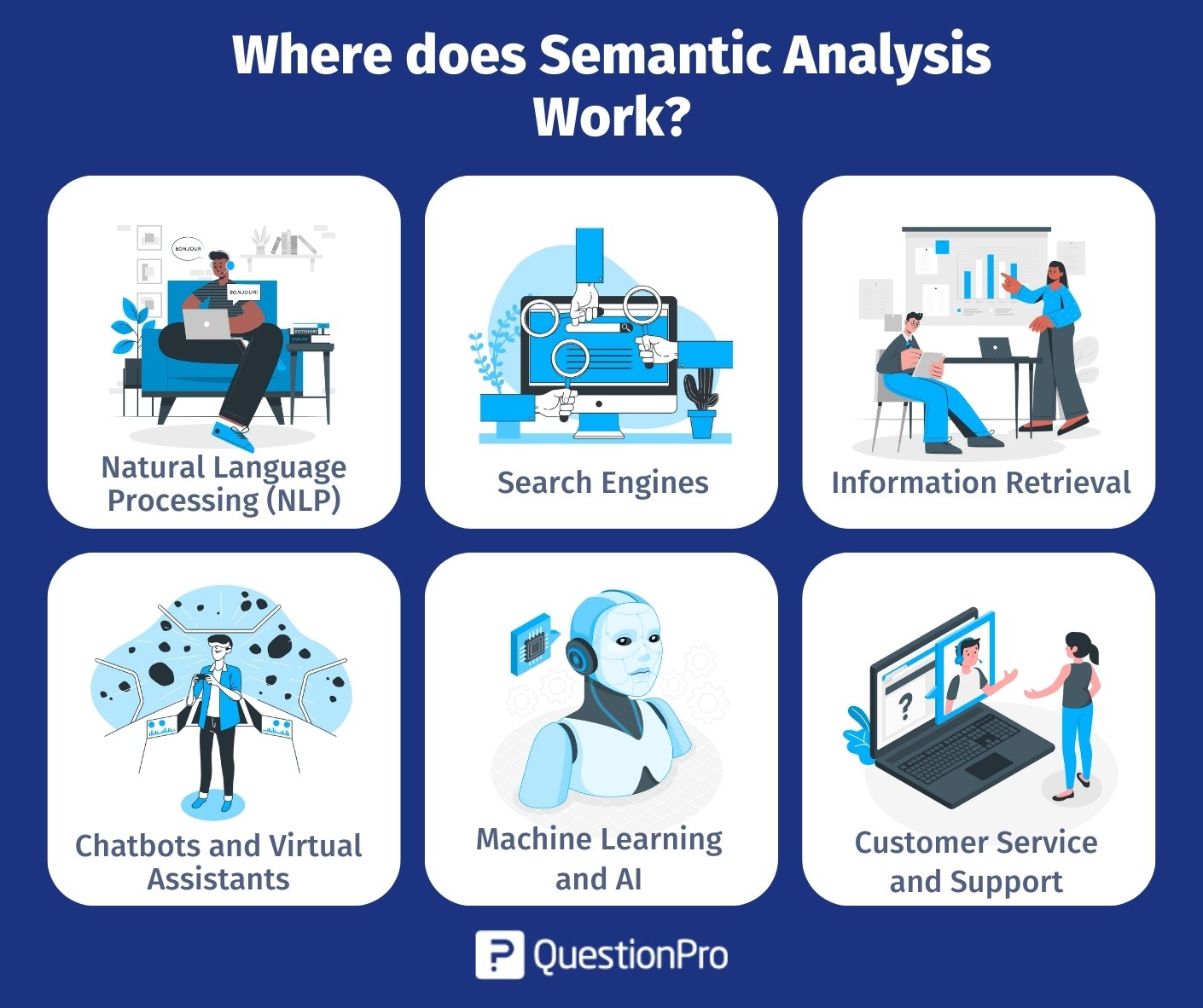
Natural Language Processing (NLP):
It’s used extensively in NLP tasks like sentiment analysis, document summarization, machine translation, and question answering, thus showcasing its versatility and fundamental role in processing language.
Search Engines:
Semantic analysis aids search engines in comprehending user queries more effectively, consequently retrieving more relevant results by considering the meaning of words, phrases, and context.
Information Retrieval:
In libraries or databases, it helps retrieve documents based on their semantic relevance rather than just keyword matching.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants:
Semantic analysis enables these systems to comprehend user queries, leading to more accurate responses and better conversational experiences.
Machine Learning and AI:
It recreates a crucial role in enhancing the understanding of data for machine learning models, thereby making them capable of reasoning and understanding context more effectively.
Customer Service and Support:
Semantic analysis aids in analyzing and understanding customer queries, helping to provide more accurate and efficient support.
Moreover, while these are just a few areas where the analysis finds significant applications. Its potential reaches into numerous other domains where understanding language’s meaning and context is crucial.
Semantic Analysis Examples
The analysis can help businesses in many ways, such as when they are dealing with customer reviews, messages from a chatbot, or conversations with a call bot. Here are some actual examples:
Uber strategically analyzes user sentiments by closely monitoring social networks when rolling out new app versions. This practice, known as “social listening,” involves gauging user satisfaction or dissatisfaction through social media channels.
“At Uber, we use this method daily to determine how our users feel about our changes. When we make a change, we immediately know what people like and what needs to be changed.”
Krzysztof Radoszewski is the Eastern and Central Europe Marketing Lead at Uber.
Example # 2: Hummingbird, Google’s semantic algorithm
Semantic analysis systems are used by more than just B2B and B2C companies to improve the customer experience. Google made its semantic tool to help searchers understand things better.
Google’s Hummingbird algorithm, made in 2013, makes search results more relevant by looking at what people are looking for.
This algorithm also boosts SEO, helping companies use quality content on their web pages. They will be linked better with keywords that are “semantically” relevant!
Can QuestionPro be helpful for Semantic Analysis Tools?
QuestionPro, a survey and research platform, might have certain features or functionalities that could complement or support the semantic analysis process.
Text Analytics and Sentiment Analysis:
QuestionPro often includes text analytics features that perform sentiment analysis on open-ended survey responses. While not a full-fledged semantic analysis tool, it can help understand the general sentiment (positive, negative, neutral) expressed within the text.
Keyword and Theme Extraction:
It may offer functionalities to extract keywords or themes from textual responses, thereby aiding in understanding the primary topics or concepts discussed within the provided text.
Data Visualization and Reporting:
Moreover, QuestionPro typically provides visualization tools and reporting features to present survey data, including textual responses. These visualizations help identify trends or patterns within the unstructured text data, supporting the interpretation of semantic aspects to some extent.
Integration with Other Tools:
Moreover, QuestionPro might connect with other specialized semantic analysis tools or NLP platforms, depending on its integrations or APIs. This integration could enhance the analysis by leveraging more advanced semantic processing capabilities from external tools.
Pairing QuestionPro’s survey features with specialized semantic analysis tools or NLP platforms allows for a deeper understanding of survey text data, yielding profound insights for improved decision-making.
Conclusion
Semantic analysis stands as the cornerstone in navigating the complexities of unstructured data, revolutionizing how computer science approaches language comprehension. Its prowess in both lexical semantics and syntactic analysis enables the extraction of invaluable insights from diverse sources.
Beyond just understanding words, it deciphers complex customer inquiries, unraveling the intent behind user searches and guiding customer service teams towards more effective responses.
Driven by the analysis, tools emerge as pivotal assets in crafting customer-centric strategies and automating processes. Moreover, they don’t just parse text; they extract valuable information, discerning opposite meanings and extracting relationships between words. Efficiently working behind the scenes, semantic analysis excels in understanding language and inferring intentions, emotions, and context.







