When conducting research, choosing the right sampling method is crucial for obtaining accurate and meaningful results. Two commonly used techniques are quota sampling vs stratified sampling. While both methods involve dividing a population into groups, they have different approaches and purposes.
In this blog, we’ll break down what they are, how they work, and when to use each in a simple and easy-to-understand way.
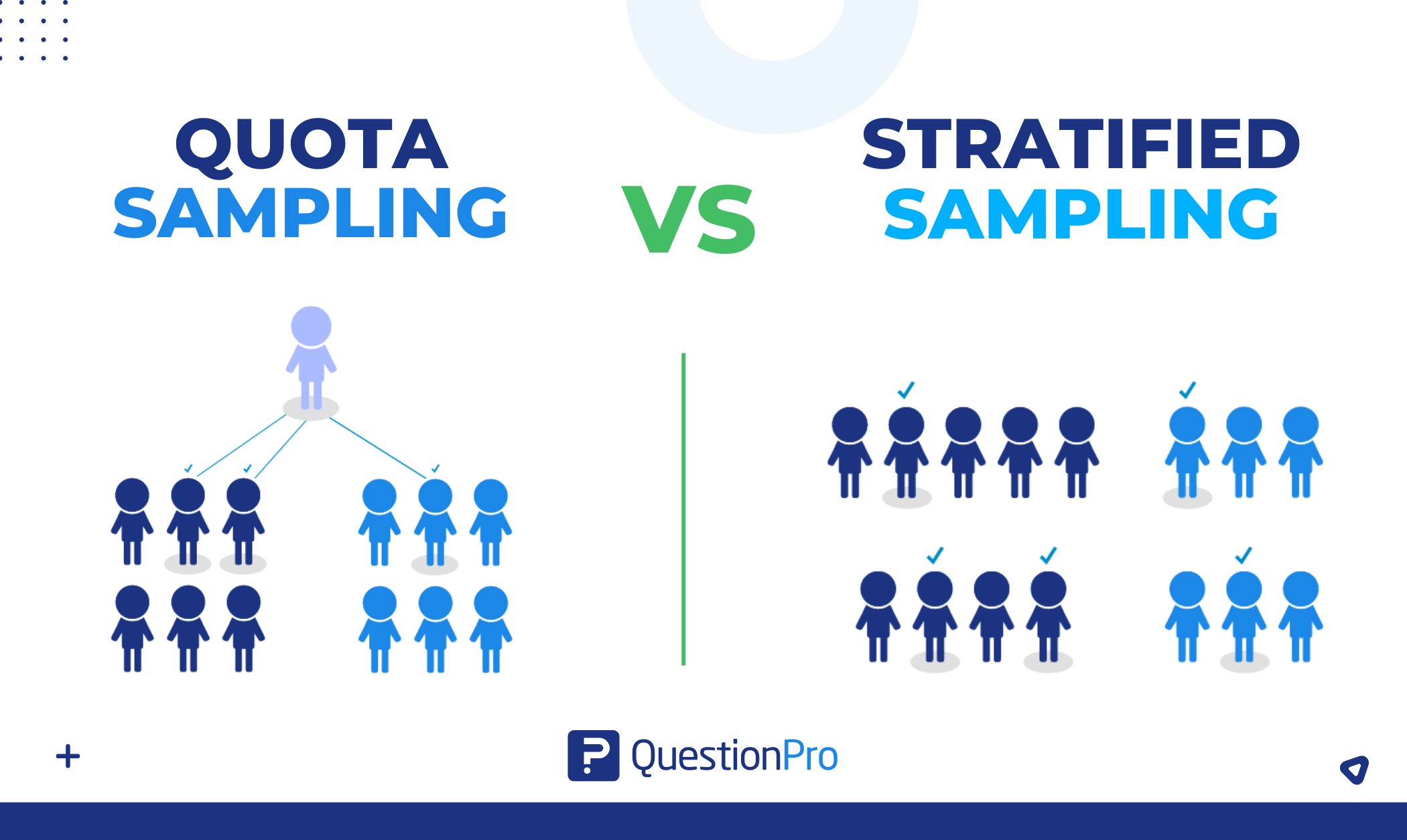
What is Quota Sampling?
Quota sampling is a method used in research where a specific number of participants are selected based on certain characteristics. Researchers divide the population into groups (like age, gender, or income level) and then choose participants to meet a set quota for each group.
For example, if a company wants to survey 100 people about a new product, they might set quotas based on demographic data such as age and gender. They could decide to include:
- 25 men aged 18-30
- 25 women aged 18-30
- 25 men aged 31-50
- 25 women aged 31-50
Instead of randomly selecting participants, researchers will actively seek individuals who match these specific criteria until each quota is filled.
Researchers use Quota Sampling because:
- It saves time and money compared to random sampling.
- You can make sure different groups are represented in the study.
- No need for a complete list of the population, which makes it practical for surveys and market research.
However, since participants are chosen non-randomly, there is a chance of sampling bias, meaning the results might not fully represent the entire population. Still, it’s a useful method when researchers need quick insights within specific groups.
Learn More: Quota Sampling: Definition, Types, Steps & Examples
What is Stratified Sampling?
Stratified sampling is a sampling method used in research projects where a population is divided into smaller groups, called strata, based on shared characteristics. After dividing the population, researchers randomly select participants from each group to ensure fair representation.
For example, if a university has 10,000 students, with 6,000 undergraduates and 4,000 postgraduates, researchers using stratified sampling would first divide the students into two strata based on their education level. Then, they would randomly select participants from each group in proportion to their size.
If they need a sample of 1,000 students, they will select:
- 600 undergraduates (60% of the sample)
- 400 postgraduates (40% of the sample)
This ensures that the sample accurately reflects the overall population distribution.
Researchers use Stratified Sampling methods because:
- It Ensures that all key subgroups are included.
- Since participants are randomly selected from each stratum, the sample better represents the population and reduces bias.
- It is great for studies where differences between groups matter.
Stratified sampling is often compared to quota sampling, but the key difference is that stratified sampling is a random sampling method, while quota sampling is non-random.
Learn More: Stratified Sampling: Definition, Types, Difference & Examples
Quota Sampling vs Stratified Sampling: What’s the Difference?
When collecting data, researchers use different methods to make sure their sample represents the population. Two common techniques are quota sampling and stratified sampling. While the techniques between quota sampling vs stratified sampling may seem similar, they have key differences that affect accuracy, reliability, and ease of use.
| Feature | Quota Sampling | Stratified Sampling |
| Selection Process | Non-random | Random |
| Bias Risk | Higher (since researchers actively select participants) | Lower (random selection reduces bias) |
| Accuracy | Less accurate | More accurate |
| Ease of Use | Quick and easy | More complex and requires planning |
| When to Use | Market research, opinion polls | Scientific studies, official reports |
Both methods have their place in research—it just depends on what matters more: speed or accuracy!
Learn More: Cluster Sampling vs Stratified Sampling
When to use Quota Sampling?
Quota sampling is a great method when you need quick, cost-effective, and targeted data collection. It works best in situations where strict randomness isn’t required, but ensuring diversity in your sample is important. Here are some common cases where quota sampling is useful:
1. Market Research & Customer Surveys
Companies often use quota sampling to gather opinions from specific customer segments. For example, if a brand is launching a new beauty product, it may survey 70% of women and 30% of men based on their expected customer base. This helps them get insights without surveying a random selection of people.
It’s faster, cheaper, and ensures the target population is included.
2. Opinion Polls & Public Surveys
News agencies and research firms use quota sampling for opinion polls before elections or social studies. They might set quotas for age, gender, or political affiliation to ensure different perspectives are represented.
It helps capture diverse views without requiring a complete list of the population.
3. Healthcare & Medical Research
Quota sampling is used in health studies when researchers need responses from specific patient groups, such as smokers vs. non-smokers or different age groups affected by a condition.
It ensures data is collected from the right groups without the complexity of random sampling.
4. Social & Behavioral Studies
Sociologists and psychologists use quota sampling when studying groups based on factors like income levels, education, or ethnicity to understand trends in human behavior.
It makes sure all relevant groups are included, even if simple random sampling isn’t possible.
5. When You Don’t Have a Full Population List
If you don’t have access to a full database of people (which is needed for stratified random sampling), quota sampling is a practical alternative.
Instead of randomly selecting participants, researchers find individuals who meet their quotas until the sample is complete.
It’s useful when a full population list is unavailable or hard to access.
Quota sampling is a great choice when researchers need quick, focused insights from specific groups. However, since participants are not chosen randomly, the results may not fully represent the entire population. If accuracy and fairness are the top priority, stratified sampling might be a better approach.
Learn More: Population vs Sample: Definition, Techniques & Differences
When to use Stratified Sampling?
Here are some common situations where stratified sampling methods or probability sampling methods are the best choice:
1. Surveys That Require Accurate Representation
When researchers need precise data that reflects the entire population, stratified sampling ensures that every important group is included in the right proportion.
It prevents overrepresentation or underrepresentation of certain groups, leading to more reliable results.
2. When Comparing Different Groups
Stratified sampling is ideal when a study aims to compare how different groups behave, think, or respond to certain situations.
It ensures equal and fair representation of all groups, leading to meaningful comparisons.
3. When Studying a Large or Diverse Population
If a population consists of people from different backgrounds, stratified sampling makes sure each subgroup is properly included.
It ensures diverse opinions and experiences are part of the study, making the results more applicable to the real world.
4. When You Need Reliable and Unbiased Data
Since participants are randomly selected within their groups, stratified sampling reduces bias and improves accuracy.
It prevents the risk of one group being overrepresented while another is overlooked.
5. When Avoiding Sampling Errors is Important
Sampling errors happen when a study doesn’t truly reflect the population. Stratified sampling helps minimize these mistakes by ensuring each category is properly represented.
It leads to higher accuracy, making the results more trustworthy.
Learn More: Survey Sampling: What it is, Types & Tips
Quota Sampling vs Stratified Sampling: Which One to Use?
Choosing between quota sampling and stratified sampling depends on your research goals. If speed and convenience sampling are your priorities, quota sampling is the way to go. However, if accuracy and fairness matter more, stratified sampling is the better choice. Understanding these differences between quota sampling vs stratified sampling will help you select the right method and get the best results for your study.
QuestionPro makes sampling easy by helping you reach the right audience with the correct method. Whether you need random, stratified, or quota-based sampling, the platform has built-in tools to ensure your data is accurate and well-represented.
Additionally, with access to a global panel of respondents, you can gather insights quickly and efficiently. Real-time analytics and automated controls take the hassle out of managing survey responses so you can focus on making informed decisions.
Right sampling is essential to conduct insightful market research. Explore quality samples with QuestionPro Audience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Answer: Use quota sampling when you need quick, cost-effective results and don’t require statistical generalizability. Use stratified sampling when you need precise, representative data for statistical analysis.
Answer: No, quota sampling is not random. Researchers choose participants based on specific quotas, which can introduce bias.
Answer: Yes, stratified sampling involves random selection within each stratum, ensuring a more representative sample.
Answer: Yes, quota sampling is commonly used in qualitative research to ensure diversity in the sample without requiring random selection.
Answer: No, quota sampling and stratified sampling are distinct methods. While both involve dividing the population into subgroups, quota sampling is non-random, and stratified sampling uses random selection.






