Empirical research is a way of learning through direct observation or experience. Instead of relying on theories or ideas alone, it gathers real-world data to understand how things work.
Researchers ask questions, conduct experiments, observe different situations, and carefully collect evidence to find answers. This method not only ensures that our beliefs are supported by facts but also reassures us that our understanding is based on solid evidence rather than mere assumptions.
In our everyday lives, we engage in informal empirical research whenever we try things and learn from the outcomes, making it an effective and relatable way to uncover the truth.
What is Empirical Research?
Empirical research depends on direct or indirect actual experience and observation as its primary source of knowledge. It focuses on collecting real-world data to answer specific research questions and solve practical problems. This method is widely used across various fields, as it helps professionals validate hypotheses with solid evidence rather than relying on assumptions.
In professional practices, empirical research is vital because it informs decisions with data-driven insights, ensuring that theories are tested and applicable in real-world scenarios.
In addition to advancing knowledge in current studies, empirical research sets a foundation for future studies. By answering specific research questions and testing new hypotheses, it continuously builds on previous findings and opens up new areas for exploration.
This empirical evidence can be gathered using quantitative market research and qualitative market research methods.
For example: A research is being conducted to find out if listening to happy music in the workplace while working may promote creativity? An experiment is conducted by using a music website survey on a set of audience who are exposed to happy music and another set who are not listening to music at all, and the subjects are then observed. The results derived from such a research will give empirical evidence if it does promote creativity or not.
Origin of Empirical Research
You must have heard the quote, “I will not believe it unless I see it.” This concept originated from the ancient empiricists, a fundamental understanding that:
- Powered the emergence of medieval science during the Renaissance period.
- Laid the foundation for modern science as we know it today.
The term “empirical” has its roots in Greek, derived from the word empirics, which means “experienced.”
In today’s world, empirical research refers to:
- The collection of data using evidence gathered through observation or experience.
- Observed and measured phenomena through experiments or by using calibrated scientific instruments.
- Reliance on previous studies and their methodology to design and validate new research.
All of these methods have one key factor in common: dependence on observation and experimentation to collect data, test hypotheses, and draw conclusions.
Empirical research can be categorized into:
- Quantitative research involves numerical data, statistical analysis, and the measurement of variables.
- Qualitative research focuses on non-numerical data and the interpretation of patterns and meanings.
In essence, empirical research relies on real-world evidence to form conclusions, distinguishing it from purely theoretical or speculative approaches.
Types And Methodologies of Empirical Research
Empirical research can be conducted and analysed using qualitative or quantitative methods.
- Quantitative research: Quantitative research methods are used to gather information through numerical data. It is used to quantify opinions, behaviors or other defined variables. These are predetermined and are in a more structured format. Some of the commonly used methods are survey, longitudinal studies, polls, etc
- Qualitative research: Qualitative research methods are used to gather non numerical data. It is used to find meanings, opinions, or the underlying reasons from its subjects. These methods are unstructured or semi structured. The sample size for such a research is usually small and it is a conversational type of method to provide more insight or in-depth information about the problem Some of the most popular forms of methods are focus groups, experiments, interviews, etc.
Data collected from these will need to be analysed. Empirical evidence can also be analysed either quantitatively and qualitatively. Using this, the researcher can answer empirical questions which have to be clearly defined and answerable with the findings he has got.
The type of research design used will vary depending on the field in which it is going to be used. Many of them might choose to do a collective research involving quantitative and qualitative method to better answer questions which cannot be studied in a laboratory setting.
Quantitative Research Methods
Quantitative research methods aid in analyzing the empirical evidence gathered. By using these a researcher can find out if his hypothesis is supported or not.
1. Survey Research
Survey research generally involves a large audience to collect a large amount of data. This is a quantitative method having a predetermined set of closed questions which are pretty easy to answer. Because of the simplicity of such a method, high responses are achieved. It is one of the most commonly used methods for all kinds of research in today’s world.
Previously, surveys were taken face to face only with maybe a recorder. However, with advancement in technology and for ease, new mediums such as emails, or social media have emerged.
For example: Depletion of energy resources is a growing concern and hence there is a need for awareness about renewable energy. According to recent studies, fossil fuels still account for around 80% of energy consumption in the United States. Even though there is a rise in the use of green energy every year, there are certain parameters because of which the general population is still not opting for green energy.
In order to understand why, a survey can be conducted to gather opinions of the general population about green energy and the factors that influence their choice of switching to renewable energy. Such a survey can help institutions or governing bodies to promote appropriate awareness and incentive schemes to push the use of greener energy.
2. Experimental Research
In experimental research, an experiment is set up and a hypothesis is tested by creating a situation in which one of the variable is manipulated. This is also used to check cause and effect. It is tested to see what happens to the independent variable if the other one is removed or altered. The process for such a method is usually proposing a hypothesis, experimenting on it, analyzing the findings and reporting the findings to understand if it supports the theory or not.
For example: A particular product company is trying to find what is the reason for them to not be able to capture the market. So the organisation makes changes in each one of the processes like manufacturing, marketing, sales and operations. Through the experiment they understand that sales training directly impacts the market coverage for their product. If the person is trained well, then the product will have better coverage.
3. Correlational Research
Correlational research is used to find relation between two set of variables. Regression analysis is generally used to predict outcomes of such a method. It can be positive, negative or neutral correlation.
For example: Higher educated individuals will get higher paying jobs. This means higher education enables the individual to high paying job and less education will lead to lower paying jobs.
4. Longitudinal Study
Longitudinal study is used to understand the traits or behavior of a subject under observation after repeatedly testing the subject over a period of time. Data collected from such a method can be qualitative or quantitative in nature.
For example: A research to find out benefits of exercise. The target is asked to exercise everyday for a particular period of time and the results show higher endurance, stamina, and muscle growth. This supports the fact that exercise benefits an individual body.
5. Cross Sectional
Cross sectional study is an observational type of method, in which a set of audience is observed at a given point in time. In this type, the set of people are chosen in a fashion which depicts similarity in all the variables except the one which is being researched.
This type does not enable the researcher to establish a cause and effect relationship as it is not observed for a continuous time period. It is majorly used by healthcare sector or the retail industry.
For example: A medical study to find the prevalence of under-nutrition disorders in kids of a given population. This will involve looking at a wide range of parameters like age, ethnicity, location, incomes and social backgrounds. If a significant number of kids coming from poor families show under-nutrition disorders, the researcher can further investigate into it. Usually a cross sectional study is followed by a longitudinal study to find out the exact reason.
6. Causal-Comparative Research
This method is based on comparison. It is mainly used to find out cause-effect relationship between two variables or even multiple variables.
For example: A researcher measured the productivity of employees in a company which gave breaks to the employees during work and compared that to the employees of the company which did not give breaks at all.
Qualitative Research Methods
Some research questions need to be analysed qualitatively, as quantitative methods are not applicable there. In many cases, in-depth information is needed or a researcher may need to observe a target audience behavior, hence the results needed are in a descriptive analysis form. Qualitative research results will be descriptive rather than predictive. It enables the researcher to build or support theories for future potential quantitative research. In such a situation qualitative research methods are used to derive a conclusion to support the theory or hypothesis being studied.
1. Case Study
Case study method is used to find more information through carefully analyzing existing cases. It is very often used for business research or to gather empirical evidence for investigation purpose. It is a method to investigate a problem within its real life context through existing cases.
The researcher has to carefully analyse making sure the parameter and variables in the existing case are the same as to the case that is being investigated. Using the findings from the case study, conclusions can be drawn regarding the topic that is being studied.
For example: A report mentioning the solution provided by a company to its client. The challenges they faced during initiation and deployment, the findings of the case and solutions they offered for the problems. Such case studies are used by most companies as it forms an empirical evidence for the company to promote in order to get more business.
2. Observational Method
Observational method is a process to observe and gather data from its target. Since it is a qualitative method it is time consuming and very personal. It can be said that observational research method is a part of ethnographic research which is also used to gather empirical evidence. This is usually a qualitative form of research, however in some cases it can be quantitative as well depending on what is being studied.
For example: setting up a research to observe a particular animal in the rain-forests of amazon. Such a research usually take a lot of time as observation has to be done for a set amount of time to study patterns or behavior of the subject. Another example used widely nowadays is to observe people shopping in a mall to figure out buying behavior of consumers.
3. One-on-one Interview
Such a method is purely qualitative and one of the most widely used. The reason being it enables a researcher get precise meaningful data if the right questions are asked. It is a conversational method where in-depth data can be gathered depending on where the conversation leads.
For example: A one-on-one interview with the finance minister to gather data on financial policies of the country and its implications on the public.
4. Focus Groups
Focus groups are used when a researcher wants to find answers to why, what and how questions. A small group is generally chosen for such a method and it is not necessary to interact with the group in person. A moderator is generally needed in case the group is being addressed in person. This is widely used by product companies to collect data about their brands and the product.
For example: A mobile phone manufacturer wanting to have a feedback on the dimensions of one of their models which is yet to be launched. Such studies help the company meet the demand of the customer and position their model appropriately in the market.
5. Text Analysis
Text analysis method is a little new compared to the other types. Such a method is used to analyse social life by going through images or words used by the individual. In today’s world, with social media playing a major part of everyone’s life, such a method enables the research to follow the pattern that relates to his study.
For example: A lot of companies ask for feedback from the customer in detail mentioning how satisfied are they with their customer support team. Such data enables the researcher to take appropriate decisions to make their support team better.
Sometimes a combination of the methods is also needed for some questions that cannot be answered using only one type of method especially when a researcher needs to gain a complete understanding of complex subject matter.
We recently published a blog that talks about examples of qualitative data in education; why don’t you check it out for more ideas?
Learn More: Data Collection Methods: Types & Examples
Steps of Conducting Empirical Research
Since empirical research is based on observation and capturing experiences, it is important to plan the steps to conduct the experiment and how to analyse it. This will enable the researcher to resolve problems or obstacles which can occur during the experiment.
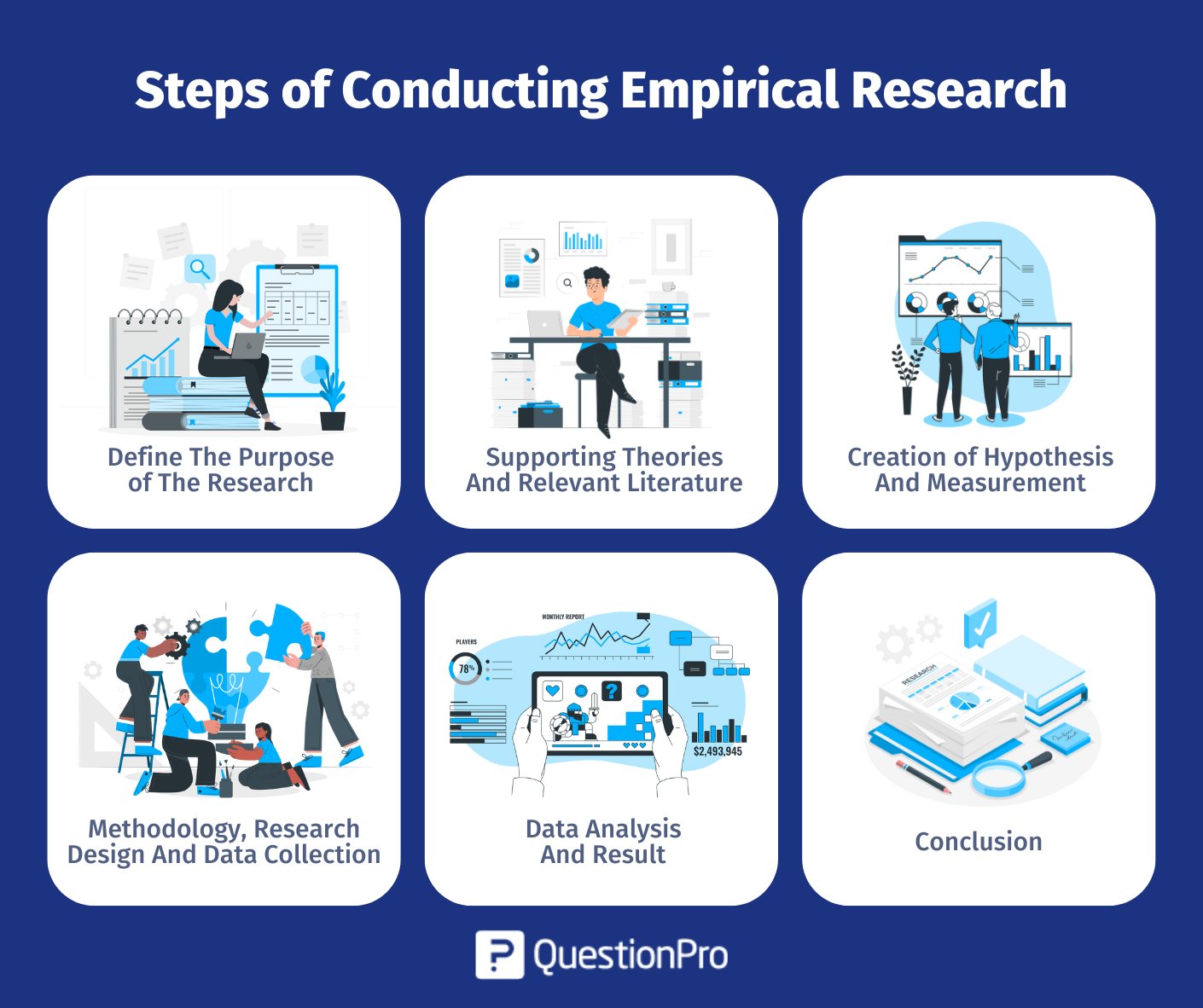
Step #1: Define The Purpose of The Research
This is the step where the researcher has to answer questions like what exactly do I want to find out? What is the problem statement? Are there any issues in terms of the availability of knowledge, data, time or resources. Will this research be more beneficial than what it will cost.
Before going ahead, a researcher has to clearly define his purpose for the research and set up a plan to carry out further tasks.
Step #2 : Supporting Theories And Relevant Literature
The researcher needs to find out if there are theories which can be linked to his research problem. He has to figure out if any theory can help him support his findings. All kind of relevant literature will help the researcher to find if there are others who have researched this before, or what are the problems faced during this research. The researcher will also have to set up assumptions and also find out if there is any history regarding his research problem
Step #3: Creation of Hypothesis And Measurement
Before beginning the actual research he needs to provide himself a working hypothesis or guess what will be the probable result. Researcher has to set up variables, decide the environment for the research and find out how can he relate between the variables.
Researcher will also need to define the units of measurements, tolerable degree for errors, and find out if the measurement chosen will be acceptable by others.
Step #4: Methodology, Research Design And Data Collection
In this step, the researcher has to define a strategy for conducting his research. He has to set up experiments to collect data which will enable him to propose the hypothesis. The researcher will decide whether he will need experimental or non experimental method for conducting the research. The type of research design will vary depending on the field in which the research is being conducted.
Last but not the least, the researcher will have to find out parameters that will affect the validity of the research design. Data collection will need to be done by choosing appropriate samples depending on the research question. To carry out the research, he can use one of the many sampling techniques. Once data collection is complete, researcher will have empirical data which needs to be analysed.
Step #5: Data Analysis And Result
Data analysis can be done in two ways, qualitatively and quantitatively. Researcher will need to find out what qualitative method or quantitative method will be needed or will he need a combination of both. Depending on the unit of analysis of his data, he will know if his hypothesis is supported or rejected. Analyzing this data is the most important part to support his hypothesis.
Step #6: Conclusion
A report will need to be made with the findings of the research. The researcher can give the theories and literature that support his research. He can make suggestions or recommendations for further research on his topic.
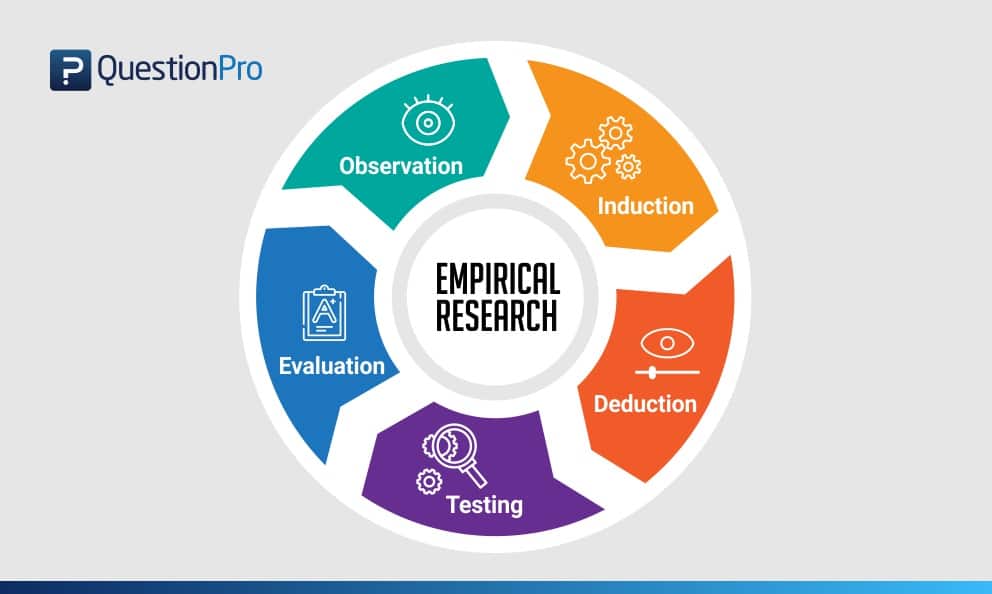
Empirical Research Methodology Cycle
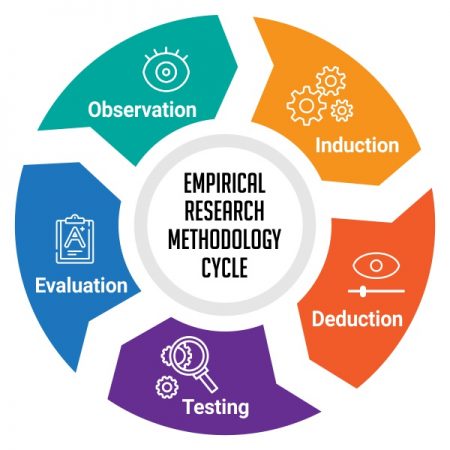
A.D. de Groot, a famous dutch psychologist and a chess expert conducted some of the most notable experiments using chess in the 1940’s. During his study, he came up with a cycle which is consistent and now widely used to conduct empirical research. It consists of 5 phases with each phase being as important as the next one.
The empirical cycle captures the process of coming up with hypothesis about how certain subjects work or behave and then testing these hypothesis against empirical data in a systematic and rigorous approach. It can be said that it characterizes the deductive approach to science. Following is the empirical cycle.
1. Observation
At this phase an idea is sparked for proposing a hypothesis. During this phase empirical data is gathered using observation. For example: a particular species of flower bloom in a different color only during a specific season.
2. Induction
Inductive reasoning is then carried out to form a general conclusion from the data gathered through observation. For example: As stated above it is observed that the species of flower blooms in a different color during a specific season. A researcher may ask a question “does the temperature in the season cause the color change in the flower?” He can assume that is the case, however it is a mere conjecture and hence an experiment needs to be set up to support this hypothesis. So he tags a few set of flowers kept at a different temperature and observes if they still change the color?
3. Deduction
This phase helps the researcher to deduce a conclusion out of his experiment. This has to be based on logic and rationality to come up with specific unbiased results.For example: In the experiment, if the tagged flowers in a different temperature environment do not change the color then it can be concluded that temperature plays a role in changing the color of the bloom.
4. Testing
This phase involves the researcher to return to empirical methods to put his hypothesis to the testing instruments. The researcher now needs to make sense of his data and hence needs to use statistical analysis plans to determine the temperature and bloom color relationship. If the researcher finds out that most flowers bloom a different color when exposed to the certain temperature and the others do not when the temperature is different, he has found support to his hypothesis. Please note this not proof but just a support to his hypothesis.
5. Evaluation
This phase is generally forgotten by most but is an important one to keep gaining knowledge. During this phase the researcher puts forth the data he has collected, the support argument and his conclusion. The researcher also states the limitations for the experiment and his hypothesis and suggests tips for others to pick it up and continue a more in-depth research for others in the future.
Pros and Cons of Empirical Research
As you may have noticed, empirical research has a lot to offer anyone who wants to conduct research and take advantage of its benefits. However, it is essential to consider not only the benefits but also the limitations and possible disadvantages you may encounter when using this methodology.
Below, we will explain both aspects a bit more so that you can consider them when conducting your research using this method.
Advantages of Empirical Research
There is a reason why empirical research is one of the most widely used method. There are a few advantages associated with it. Following are a few of them.
- It is used to authenticate traditional research through various experiments and observations.
- This research methodology makes the research being conducted more competent and authentic.
- It enables a researcher understand the dynamic changes that can happen and change his strategy accordingly.
- The level of control in such a research is high so the researcher can control multiple variables.
- It plays a vital role in increasing internal validity.
Disadvantages of Empirical Research
Even though empirical research makes the research more competent and authentic, it does have a few disadvantages. Following are a few of them.
- Such a research needs patience as it can be very time consuming. The researcher has to collect data from multiple sources and the parameters involved are quite a few, which will lead to a time consuming research.
- Most of the time, a researcher will need to conduct research at different locations or in different environments, this can lead to an expensive affair.
- There are a few rules in which experiments can be performed and hence permissions are needed. Many a times, it is very difficult to get certain permissions to carry out different methods of this research.
- Collection of data can be a problem sometimes, as it has to be collected from a variety of sources through different methods.
Empirical Research Vs Non-Empirical Research
Empirical and non-empirical research are two fundamental approaches in research methodology. Understanding their key differences helps researchers choose the appropriate method based on their research objectives.
| Feature | Empirical Research | Non-Empirical Research |
| Definition | Based on observed and measured phenomena. | Based on existing knowledge, logic, and reasoning. |
| Data Collection | Directly gathers new data through experiments, surveys, or observations. | Uses secondary data, theoretical analysis, or literature reviews. |
| Analysis | Quantitative, often statistical. | Conceptual or theoretical interpretation. |
| Examples | Controlled experiments, field studies, surveys. | Literature reviews, meta-analyses, theoretical research. |
| Goal | To confirm or refute hypotheses with empirical evidence. | To synthesize existing information, propose theories. |
| Evidence Type | Observable and measurable. | Conceptual, theoretical, or synthesized. |
Both empirical and non-empirical research offers valuable insights and contribute uniquely to knowledge. Together, they form a comprehensive approach to exploring, explaining, and expanding knowledge across disciplines.
Why is There a Need for Empirical Research?
Empirical research is important today because most people believe in something only when they can see, hear, or experience it. It is used to validate multiple hypotheses, derive knowledge, and increase human understanding, and it is continuing to do so to advance in various fields.
This often involves using testing instruments to ensure the accuracy and reliability of data collection, especially when it comes to complex variables.
In addition, research participants’ discussion often plays a key role in understanding the results and validating the findings within a theoretical framework that guides the entire study.
Qualitative methods are frequently used to gain deeper insights into participants’ perspectives, helping to contextualize empirical data. A literature review, or multiple literature reviews, also helps ground the research in existing knowledge, linking the new findings with past studies.
For example, pharmaceutical companies use empirical research to test specific drugs on controlled or random groups, using both qualitative methods and testing instruments to study cause and effect. This way, they prove certain theories they had proposed for the specific drug.
Such research is very important, as sometimes it can lead to finding a cure for a long-standing disease. In addition, the use of statistical data is essential for validating results and ensuring their reliability. Empirical research is useful in science, social sciences, business, and many other fields, like history, deriving knowledge through quantitative and qualitative methods.
Use QuestionPro Research Suite for Empirical Research
Using QuestionPro Research Suite for empirical research makes the process easier and more efficient. Here’s why:
01. User-Friendly Data Collection Tools
QuestionPro’s suite of tools, including surveys, polls, and questionnaires, are designed with user-friendliness in mind, making it a breeze to gather real-world data from diverse sources.
02. Highly Customizable
This lets you personalize surveys per your research requirements, ensuring the collected data is always relevant and valuable.
03. Real-Time Analytics
Get immediate feedback with QuestionPro real-time analytics to see trends and patterns in your data immediately
4. Even Better Data Management
The most efficient way of managing large sets of data is to keep the analysis and its outcomes faster and more reliable.
Overall, QuestionPro simplifies the empirical research process and allows you to focus more on data analysis and interpretation than manual collection and organization.
Conclusion About Empirical Research
Empirical research is a tool for understanding data and deducing its meaning. By focusing on what can be measured or experienced, we are better equipped to think critically and develop practical solutions.
When identifying empirical research, we focus on real-world data and its key characteristics, such as observation, experimentation, and evidence-based conclusions. The research process involves careful data collection, analysis, and the ability to communicate empirical research findings.
In doing so, we can make sense of the data and our feelings, leading to more informed decisions. Ultimately, empirical research enables us to transition from mere assumptions to solid evidence. Identifying patterns and validating hypotheses can improve outcomes in scientific and daily fields.
Frequently Asked Questions( FAQs)
Empirical research is a type of study that relies on observation, experience, or experimentation to gather data. It involves collecting evidence through direct or indirect observation of real-world phenomena and analyzing that data to form conclusions, often using scientific methods such as experiments or surveys.
Examples of empirical research include:
1. Conducting experiments to test a scientific hypothesis.
2. Surveying individuals to gather opinions or behaviors.
3. Observing wildlife in their natural environment.
4. Measuring the effects of a treatment in a clinical trial.
5. Analyzing historical data to identify trends or patterns.
Empirical research relies on observation and data collection through experiments or real-world evidence, whether quantitative (numerical) or qualitative (non-numerical).
Qualitative research, a subset of empirical research, focuses specifically on understanding patterns, behaviors, and experiences through non-numerical data like interviews, observations, or texts.







