
Data is a collection of facts, figures, objects, symbols, and events from different sources. Organizations collect data using various methods to make better decisions. Without data, it would be difficult for organizations to make appropriate decisions, so data is collected from different audiences at various times.
For example, an organization must collect data on product demand, customer preferences, and competitors before launching a new product. If data is not collected beforehand, the organization’s newly launched product may fail for many reasons, such as less demand and inability to meet customer needs.
Although data is a valuable asset for every organization, it does not serve any purpose until it is analyzed or processed to achieve the desired results.
What are Data Collection Methods?
Data collection methods are techniques and procedures for gathering information for research purposes. They can range from simple self-reported surveys to more complex quantitative or qualitative experiments.
Some common data collection methods include surveys, interviews, observations, focus groups, experiments, and secondary data analysis. The data collected through these methods can then be analyzed to support or refute research hypotheses and draw conclusions about the study’s subject matter.
Understanding Data Collection Methods
Data collection methods encompass a variety of techniques and tools for gathering quantitative and qualitative data. These methods are integral to the data collection and ensure accurate and comprehensive data acquisition.
Quantitative data collection methods involve systematic approaches, such as
- Numerical data,
- Surveys, polls and
- Statistical analysis
- To quantify phenomena and trends.
Conversely, qualitative data collection methods focus on capturing non-numerical information, such as interviews, focus groups, and observations, to delve deeper into understanding attitudes, behaviors, and motivations.
Combining quantitative and qualitative data collection techniques can enrich organizations’ datasets and gain comprehensive insights into complex phenomena.
Effective utilization of accurate data collection tools and techniques enhances the accuracy and reliability of collected data, facilitating informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Learn more about what is Self-Selection Bias, methods & its examples
Importance of Data Collection Methods
Data collection methods play a crucial role in the research process as they determine the quality and accuracy of the data collected. Here are some major importance of data collection methods.
- Quality and Accuracy: The choice of data collection technique directly impacts the quality and accuracy of the data obtained. Properly designed methods help ensure that the data collected is error-free and relevant to the research questions.
- Relevance, Validity, and Reliability: Effective data collection methods help ensure that the data collected is relevant to the research objectives, valid (measuring what it intends to measure), and reliable (consistent and reproducible).
- Bias Reduction and Representativeness: Carefully chosen data collection methods can help minimize biases inherent in the research process, such as sampling or response bias. They also aid in achieving a representative sample, enhancing the findings’ generalizability.
- Informed Decision Making: Accurate and reliable data collected through appropriate methods provide a solid foundation for making informed decisions based on research findings. This is crucial for both academic research and practical applications in various fields.
- Achievement of Research Objectives: Data collection methods should align with the research objectives to ensure that the collected data effectively addresses the research questions or hypotheses. Properly collected data facilitates the attainment of these objectives.
- Support for Validity and Reliability: Validity and reliability are essential to research validity. The choice of data collection methods can either enhance or detract from the validity and reliability of research findings. Therefore, selecting appropriate methods is critical for ensuring the credibility of the research.
The importance of data collection methods cannot be overstated, as they play a key role in the research study’s overall success and internal validity.
Types of Data Collection Methods
The choice of data collection method depends on the research question being addressed, the type of data needed, and the resources and time available. Data collection methods can be categorized into primary and secondary methods.
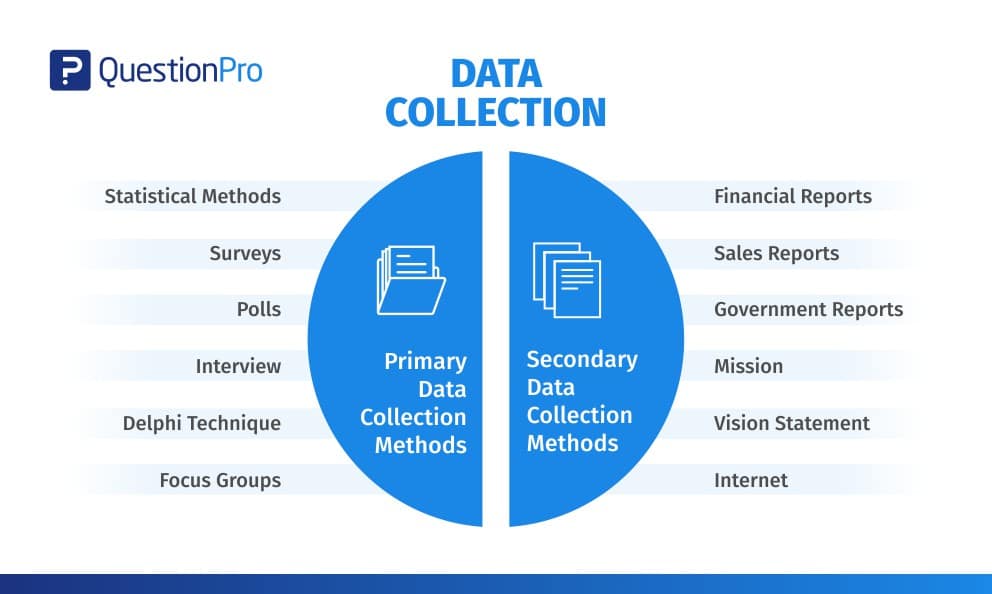
1. Primary Data Collection Methods
Primary data is collected from first-hand experience and is not used in the past. The data gathered by primary data collection methods are highly accurate and specific to the research’s motive.
Primary data collection methods can be divided into two categories: quantitative and qualitative.
Quantitative Methods:
Quantitative techniques for market research and demand forecasting usually use statistical tools. In these techniques, demand is forecasted based on historical data. These methods of primary data collection are generally used to make long-term forecasts. Statistical analysis methods are highly reliable as subjectivity is minimal.
- Time Series Analysis: A time series refers to a sequential order of values of a variable, known as a trend, at equal time intervals. Using patterns, an organization can predict the demand for its products and services over a projected time period.
- Smoothing Techniques: Smoothing techniques can be used in cases where the time series lacks significant trends. They eliminate random variation from the historical demand, helping identify patterns and demand levels to estimate future demand.
The most common methods used in smoothing demand forecasting are the simple moving average and weighted moving average methods. - Barometric Method: Also known as the leading indicators approach, researchers use this method to speculate future trends based on current developments. When past events are considered to predict future events, they act as leading indicators.

Qualitative Methods:
Qualitative data collection methods are especially useful when historical data is unavailable or when numbers or mathematical calculations are unnecessary.
Qualitative research is closely associated with words, sounds, feelings, emotions, colors, and non-quantifiable elements. These techniques are based on experience, judgment, intuition, conjecture, emotion, etc.
Quantitative methods do not provide the motive behind participants’ responses, often don’t reach underrepresented populations, and require long periods of time to collect the data. Hence, it is best to combine quantitative methods with qualitative methods.
1. Surveys: Surveys collect data from the target audience and gather insights into their preferences, opinions, choices, and feedback related to their products and services. Most survey software offers a wide range of question types.
You can also use a ready-made survey template to save time and effort. Online surveys can be customized to match the business’s brand by changing the theme, logo, etc. They can be distributed through several channels, such as email, website, offline app, QR code, social media, etc.
You can select the channel based on your audience’s type and source. Once the data is collected, survey software can generate reports and run analytics algorithms to discover hidden insights.
A survey dashboard can give you statistics related to response rate, completion rate, demographics-based filters, export and sharing options, etc. Integrating survey builders with third-party apps can maximize the effort spent on online real-time data collection.
Practical business intelligence relies on the synergy between analytics and reporting, where analytics uncovers valuable insights, and reporting communicates these findings to stakeholders.
2. Polls: Polls comprise one single or multiple-choice question. They are useful when you need to get a quick pulse of the audience’s sentiments. Because they are short, it is easier to get responses from people.
Like surveys, online polls can be embedded into various platforms. Once the respondents answer the question, they can also be shown how their responses compare to others.
Interviews: In this method, the interviewer asks the respondents face-to-face or by telephone.
3. Interviews: In face-to-face interviews, the interviewer asks a series of questions to the interviewee in person and notes down responses. If it is not feasible to meet the person, the interviewer can go for a telephone interview.
This form of data collection is suitable for only a few respondents. It is too time-consuming and tedious to repeat the same process if there are many participants.

4. Delphi Technique: In the Delphi method, market experts are provided with the estimates and assumptions of other industry experts’ forecasts. Based on this information, experts may reconsider and revise their estimates and assumptions. The consensus of all experts on demand forecasts constitutes the final demand forecast.
5. Focus Groups: Focus groups are one example of qualitative data in education. In a focus group, a small group of people, around 8-10 members, discuss the common areas of the research problem. Each individual provides his or her insights on the issue concerned.
A moderator regulates the discussion among the group members. At the end of the discussion, the group reaches a consensus.
6. Questionnaire: A questionnaire is a printed set of open-ended or closed-ended questions that respondents must answer based on their knowledge and experience with the issue. The questionnaire is part of the survey, whereas the questionnaire’s end goal may or may not be a survey.
7. Digsite: Digsite is a purpose-built platform for conducting fast and flexible qualitative research, enabling users to understand the ‘whys’ behind consumer behavior. With Digsite, businesses can efficiently recruit targeted participants and gather rich qualitative insights through various methods, such as
- Live video interviews,
- Polls and
- Focus groups.
The platform supports agile, iterative learning by blending surveys, open-ended research, and intelligent dashboards for actionable results. Its natural language processing (NLP) and AI capabilities offer deeper emotional insights, enhancing user experience and product development. Supporting over 50 languages and ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA, Digsite provides a secure and comprehensive research solution.
2. Secondary Data Collection Methods
Secondary data is data that has been used in the past. The researcher can obtain data from the data sources, both internal and external, to the organizational data.
Internal sources of secondary data:
- Organization’s health and safety records
- Mission and vision statements
- Financial Statements
- Magazines
- Sales Report
- CRM Software
- Executive summaries
External sources of secondary data:
- Government reports
- Press releases
- Business journals
- Libraries
- Internet
Secondary data collection methods can also involve quantitative and qualitative techniques. Secondary data is easily available, less time-consuming, and expensive than primary data. However, the authenticity of the data gathered cannot be verified using these methods.
Secondary data collection methods can also involve quantitative and qualitative observation techniques. Secondary data is easily available, less time-consuming, and more expensive than primary data.
However, the authenticity of the data gathered cannot be verified using these methods.
Regardless of the data collection method of your choice, there must be direct communication with decision-makers so that they understand and commit to acting according to the results.
For this reason, we must pay special attention to the analysis and presentation of the information obtained. Remember that these data must be useful and functional to us, so the data collection method has much to do with it.
LEARN ABOUT: Data Asset Management: What It Is & How to Manage It
Steps in the Data Collection Process
The data collection process typically involves several key steps to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data gathered. These steps provide a structured approach to gathering and analyzing data effectively. Here are the key steps in the data collection process:
- Define the Objectives: Clearly outline the goals of the data collection. What questions are you trying to answer?
- Identify Data Sources: Determine where the data will come from. This could include surveys, interviews, existing databases, or observational data.
- Choose Data Collection Methods: Select appropriate methods based on your objectives and data sources. Common methods include:
- Surveys and questionnaires
- Interviews (structured or unstructured)
- Focus groups
- Observational Research
- Document analysis
- Develop Data Collection Instruments: Create or adapt tools for collecting data, such as questionnaires or interview guides. Ensure they are valid and reliable.
- Select a Sample: If you are not collecting data from the entire population, determine how to select your sample. Consider sampling methods like random, stratified, or convenience sampling.
- Collect Data: Execute your data collection plan, following ethical collection guidelines and maintaining data integrity.
- Store Data: Organize and store collected data securely, ensuring it’s easily accessible for analysis while maintaining confidentiality.
- Analyze Data: After collecting the data, process and analyze it according to your objectives, using appropriate statistical or qualitative methods.
- Interpret Results: Conclude your analysis, relating them back to your original objectives and research questions.
- Report Findings: Present your findings clearly and organized, using visuals and summaries to communicate insights effectively.
- Evaluate the Process: Reflect on the data collection process. Assess what worked well and what could be improved for future studies.
Recommended Data Collection Tools
Choosing the right data collection tools depends on your specific needs, such as the type of data you’re collecting, the scale of your project, and your budget. Here are some widely used tools across different categories:
Survey Tools
Survey tools are software applications designed to collect quantitative data from a large audience through structured questionnaires. These tools are ideal for gathering customer feedback, employee opinions, or market research insights. They offer features like customizable templates, real-time analytics, and multiple distribution channels to help you reach your target audience effectively.
- QuestionPro: Offers advanced survey features and analytics.
- SurveyMonkey: User-friendly interface with customizable survey options.
- Google Forms: Free and easy to use, suitable for simple surveys.
Interview and Focus Group Tools
Interview and focus group tools facilitate the collection of qualitative data through guided conversations and group discussions. These tools often include features for recording, transcribing, and analyzing spoken interactions, enabling researchers to gain in-depth insights into participants’ thoughts, attitudes, and behaviors.
- Zoom: Great for virtual interviews and focus group discussions.
- Microsoft Teams: Offers features for collaboration and recording sessions.
Observation and Field Data Collection
Interview and focus group tools facilitate the collection of qualitative data through guided conversations and group discussions. These tools often include features for recording, transcribing, and analyzing spoken interactions, enabling researchers to gain in-depth insights into participants’ thoughts, attitudes, and behaviors.
- Open Data Kit (ODK): This is for mobile data collection in field settings.
- REDCap: A secure web application for building and managing online surveys.
Mobile Data Collection
Mobile data collection tools leverage smartphones and tablets to gather data on the go. These tools enable users to collect data offline and sync it when an internet connection is available. They are ideal for remote areas or fieldwork where traditional data collection methods are impractical, offering features like GPS tagging, photo capture, and form-based inputs.
- KoboToolbox: Designed for humanitarian work, useful for field data collection.
- SurveyCTO: Provides offline data collection capabilities for mobile devices.
Data Analysis Tools
Data analysis tools are software applications that process and analyze quantitative data, helping researchers identify patterns, trends, and insights. These tools support various statistical methods and data visualization techniques, allowing users to interpret data effectively and make informed decisions based on their findings.
- Tableau: Powerful data visualization tool to analyze survey results.
- SPSS: Widely used for statistical analysis in research.
Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative data analysis tools help researchers organize, code, and interpret non-numerical data, such as text, images, and videos. These tools are essential for analyzing interview transcripts, open-ended survey responses, and social media content, providing features like thematic analysis, sentiment analysis, and visualization of qualitative patterns.
- NVivo: For analyzing qualitative data like interviews or open-ended survey responses.
- Dedoose: Useful for mixed-methods research, combining qualitative and quantitative data.
General Data Collection and Management
General data collection and management tools provide a comprehensive solution for collecting, storing, and organizing data from various sources. These tools often include features for data integration, cleansing, and security, ensuring that data is accessible and usable for analysis across different departments and projects. They are ideal for organizations looking to streamline their data management processes and enhance collaboration.
- Airtable: Combines spreadsheet and database functionalities for organizing data.
- Microsoft Excel: A versatile tool for data entry, analysis, and visualization.
If you are interested in purchasing, we invite you to visit our article, where we dive deeper and analyze the best data collection tools in the industry.
How Can QuestionPro Help to Create Effective Data Collection?
QuestionPro is a comprehensive online survey software platform that can greatly assist in various data collection methods. Here’s how it can help:
- Survey Creation: QuestionPro offers a user-friendly interface for creating surveys with various question types, including multiple-choice, open-ended, Likert scale, and more. Researchers can customize surveys to fit their specific research needs and objectives.
- Diverse Distribution Channels: The platform provides multiple channels for distributing surveys, including email, web links, social media, and website embedding surveys. This enables researchers to reach a wide audience and collect data efficiently.
- Panel Management: QuestionPro offers panel management features, allowing researchers to create and manage panels of respondents for targeted data collection. This is particularly useful for longitudinal studies or when targeting specific demographics.
- Data Analysis Tools: The platform includes robust data analysis tools that enable researchers to analyze survey responses in real time. Researchers can generate customizable reports, visualize data through charts and graphs, and identify trends and patterns within the data.
- Data Security and Compliance: QuestionPro prioritizes data security and compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA. The platform offers features such as SSL encryption, data masking, and secure data storage to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of collected data.
- Mobile Compatibility: With the increasing use of mobile devices, QuestionPro ensures that surveys are mobile-responsive, allowing respondents to participate in surveys conveniently from their smartphones or tablets.
- Integration Capabilities: QuestionPro integrates with various third-party tools and platforms, including CRMs, email marketing software, and analytics tools. This allows researchers to streamline their data collection processes and incorporate survey data into their existing workflows.
- Customization and Branding: Researchers can customize surveys with their branding elements, such as logos, colors, and themes, enhancing the professional appearance of surveys and increasing respondent engagement.
Conclusion
The conclusion you obtain from your investigation will set the course of the company’s decision-making, so present your report clearly and list the steps you followed to obtain those results.
Make sure that whoever will take the corresponding actions understands the importance of the information collected and that it gives them the solutions they expect.
QuestionPro offers a comprehensive suite of features and tools that can significantly streamline the data collection process, from survey creation to analysis, while ensuring data security and compliance. Remember that at QuestionPro, we can help you collect data easily and efficiently. Request a demo and learn about all the tools we have for you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A: Common methods include surveys, interviews, observations, focus groups, and experiments.
A: Data collection helps organizations make informed decisions and understand trends, customer preferences, and market demands.
A: Quantitative methods focus on numerical data and statistical analysis, while qualitative methods explore non-numerical insights like attitudes and behaviors.
A: Yes, combining methods can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the research topic.
A: Technology streamlines data collection with tools like online surveys, mobile data gathering, and integrated analytics platforms.







