
Descriptive research and Correlational research are two important types of research studies that help researchers make ambitious and measured decisions in their respective fields. Both descriptive research and correlational research are used in descriptive correlational research.
Descriptive research is defined as a research method that involves observing behavior to describe attributes objectively and systematically. A descriptive research project seeks to comprehend phenomena or groups in depth.
Correlational research, on the other hand, is a method that describes and predicts how variables are naturally related in the real world without the researcher attempting to alter them or assign causation between them.
The main objective of descriptive research is to create a snapshot of the current state of affairs, whereas correlational research helps in comparing two or more entities or variables.
What is descriptive correlational research?
Descriptive correlational research is a type of research design that tries to explain the relationship between two or more variables without making any claims about cause and effect. It includes collecting and analyzing data on at least two variables to see if there is a link between them.
In descriptive correlational research, researchers collect data to explain the variables of interest and figure out how they relate. The main goal is to give a full account of the variables and how they are related without changing them or assuming that one thing causes another.
In descriptive correlational research, researchers do not change any variables or try to find cause-and-effect connections. Instead, they just watch and measure the variables of interest and then look at the patterns and relationships that emerge from the data.
Experimental research involves the independent variable to see how it affects the dependent variable, while descriptive correlational research just describes the relationship between variables.
In descriptive correlational research, correlational research designs measure the magnitude and direction of the relationship between two or more variables, revealing their associations. At the outset creating initial equivalence between the groups or variables being compared is essential in descriptive correlational research
The independent variable occurs prior to the measurement of the measured dependent variable in descriptive correlational research. Its goal is to explain the traits or actions of a certain population or group and look at the connections between independent and dependent variables.
How are descriptive research and correlational research carried out?
Descriptive research is carried out using three methods, namely:
- Case studies– Case studies involve in-depth research and study of individuals or groups. Case studies lead to a hypothesis and widen a further scope of studying a phenomenon. However, case studies should not be used to determine cause and effect as they don’t have the capacity to make accurate predictions.
- Surveys– A survey is a set of questions that is administered to a population, also known as respondents. Surveys are a popular market research tool that helps collect meaningful insights from the respondents. To gather good quality data, a survey should have good survey questions, which should be a balanced mix of open-ended and close-ended questions.
- Naturalistic Observation– Naturalistic observations are carried out in the natural environment without disturbing the person/ object in observation. It is much like taking notes about people in a supermarket without letting them know. This leads to a greater validity of collected data because people are unaware they are being observed here. This tends to bring out their natural characteristics.
Correlational research also uses naturalistic observation to collect data. However, in addition, it uses archival data to gather information. Archival data is collected from previously conducted research of a similar nature. Archival data is collected through primary research.
In contrast to naturalistic observation, information collected through archived is straightforward. For example, counting the number of people named Jacinda in the United States using their social security number.
Descriptive Research vs Correlational Research
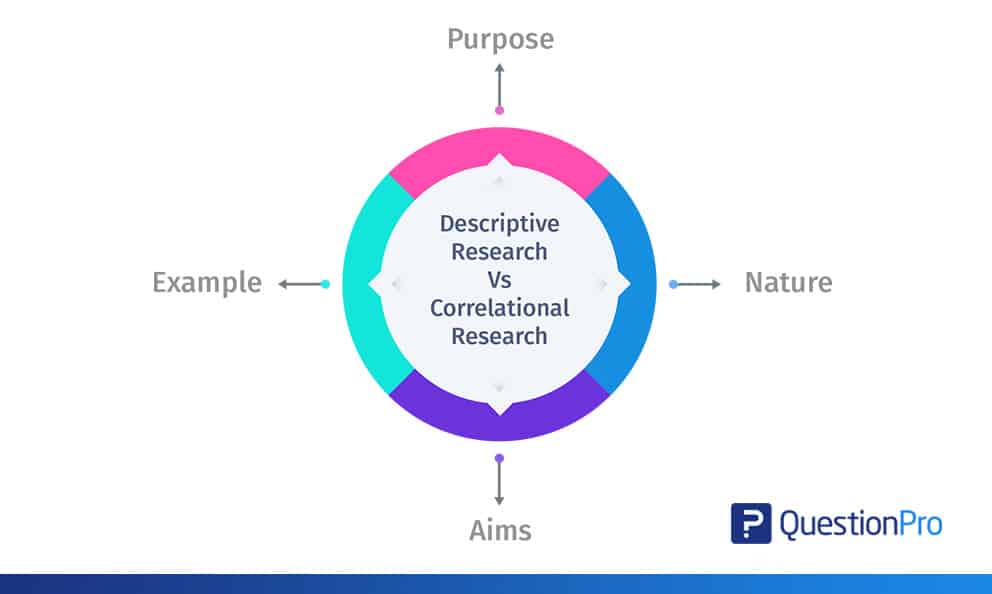
| Attributes | Descriptive Research | Correlational Research |
| Purpose | Descriptive research is used to uncover new facts and the meaning of research. | Correlational research is carried out to measure two variables. |
| Nature | Descriptive research is analytical, where in-depth studies help collect information during research. | Correlational nature is mathematical in nature. A positive correlation appears coefficient to statistically measure the relationship between two variables. |
| Aims | Descriptive nature provides a knowledge base for carrying out other quantitative research | This type of research is used to explore the extent to which two variables in a study are related. |
| Example | Research was done to obtain information on the hospitality industry’s most widely used employee motivation tools. | Research has been done to know if cancer and marriage are related. |
Features of Descriptive Correlational Research
The key features of descriptive correlational research include the following:

01. Description
The main goal, just like with descriptive research, is to describe the variables of interest thoroughly. Researchers aim to explain a certain group or event’s traits, behaviors, or attitudes.
02. Relationships
Like correlational research, descriptive correlational research looks at how two or more factors are related. It looks at how variables are connected to each other, such as how they change over time or how they are linked.
03. Quantitative analysis
Most methods for analyzing quantitative analysis data are used in descriptive correlational research. Researchers use statistical methods to study and measure the size and direction of relationships between variables.
04. No manipulation
As with correlational research, the researcher does not change or control the variables. The data is taken in its natural environment without any changes or interference.
05. Cross-sectional or longitudinal
Cross-sectional or longitudinal designs can be used for descriptive correlational research. It collects data at one point in time, while longitudinal research collects data over a long period of time to look at changes and relationships over time.
Examples of descriptive correlational research
For example, descriptive correlational research could look at the link between a person’s age and how much money they make. The researcher would take a sample of people’s ages and incomes and then look at the data to see if there is a link between the two factors.
- Example 1: A research project is done to find out if there is a link between how long college students sleep and how well they do in school. They keep track of how many hours kids sleep each night and what their GPAs are. By studying the data, the researcher can describe how the students sleep and find out if there is a link between how long they sleep and how well they do in school.
- Example 2: A researcher wants to know how people’s exercise habits affect their physical health if they are between the ages of 40 and 60. They take notes on things like how often and how hard you work out, your body mass index (BMI), blood pressure, and cholesterol numbers. By analyzing the data, the researcher can describe the participants’ exercise habits and physical health and look for any links between these factors.
- Example 3: Let’s say a researcher wants to find out if college students who work out feel less stressed. Using a poll, the researcher finds out how many hours students spend exercising each week and how stressed they feel. By looking at the data, the researcher may find that there is a moderate negative correlation between exercise and stress levels. This means that as exercise grows, stress levels tend to go down.
Conclusion
Descriptive correlational research is a good way to learn about the characteristics of a population or group and the relationships between its different parts. It lets researchers describe variables in detail and look into their relationships without suggesting that one variable caused another.
Descriptive correlational research gives useful insights and can be used as a starting point for more research or to come up with hypotheses. It’s important to be aware of the problems with this type of study, such as the fact that it can’t show cause and effect and relies on cross-sectional data.
Still, descriptive correlational research helps us understand things and makes making decisions in many areas easier.
QuestionPro is a very useful tool for descriptive correlational research. Its many features and easy-to-use interface help researchers collect and study data quickly, giving them a better understanding of the characteristics and relationships between variables in a certain population or group.
The different kinds of questions, analytical research tools, and reporting features on the software improve the research process and help researchers come up with useful results. QuestionPro makes it easier to do descriptive correlational research, which makes it a useful tool for learning important things and making decisions in many fields.







