Do you think you have an excellent idea for a product that will break down barriers and be a massive hit in the online market? But how can you make sure people will buy your product? This is when product testing comes in.
Product Testing is a methodology that can help you figure out how to make a successful product. It also lets you figure out if your first idea will work to ensure that customers like each new version of your product.
Testing tips are grouped based on the product type, the specific parts of the product you want to test, where the testing is done, and what stage of development the product is in.
This article discusses the different types of products, gives tips for testing them, and explains why they are vital for your business.
What is Product Testing?
Product testing is a methodology used to determine all aspects of a product, how it is made, or how well it works. This helps companies make sure that their products meet the needs of a wide range of customers before they start making them.
Companies should have a clear idea of what needs to be added to the product, i.e., they’ll know what the customers want to see to improve the product.
Testing products allows brands to learn how customers might use the product, what they like, what they expect, and how they react. It helps you determine how your target customers feel about your product, whether online or in the real world.
Now that we’ve understood the concept of Product Testing let’s take a closer look at some important details to comprehend its significance and how you can leverage it in your launches.
FAQs about Product Testing 🧠 ▼
Importance of Product Testing
When looking for reliable insights and expertise, partnering with the best product testing companies can significantly enhance your product development process. Testing products can be helpful in many different ways, including the following:
- A product testing website helps to find out how products change as they get older. It also ensures that effects can last for a long time, which is especially important for businesses dealing with technology.
- It can also keep an eye on possible threats from competing products. Testing can find flaws in product development and compare how it works in different settings and environments.
- It can also be used on customers. This should tell you if an item will sell well or if it still needs work before it can be sold to the general public. Market testing falls under the same category, and companies can predict how customers will react to new products.
Types of Product Testing
Testing can vary depending on the project, but some types of testing are the same across many different fields. Here are some common ways to test a product.
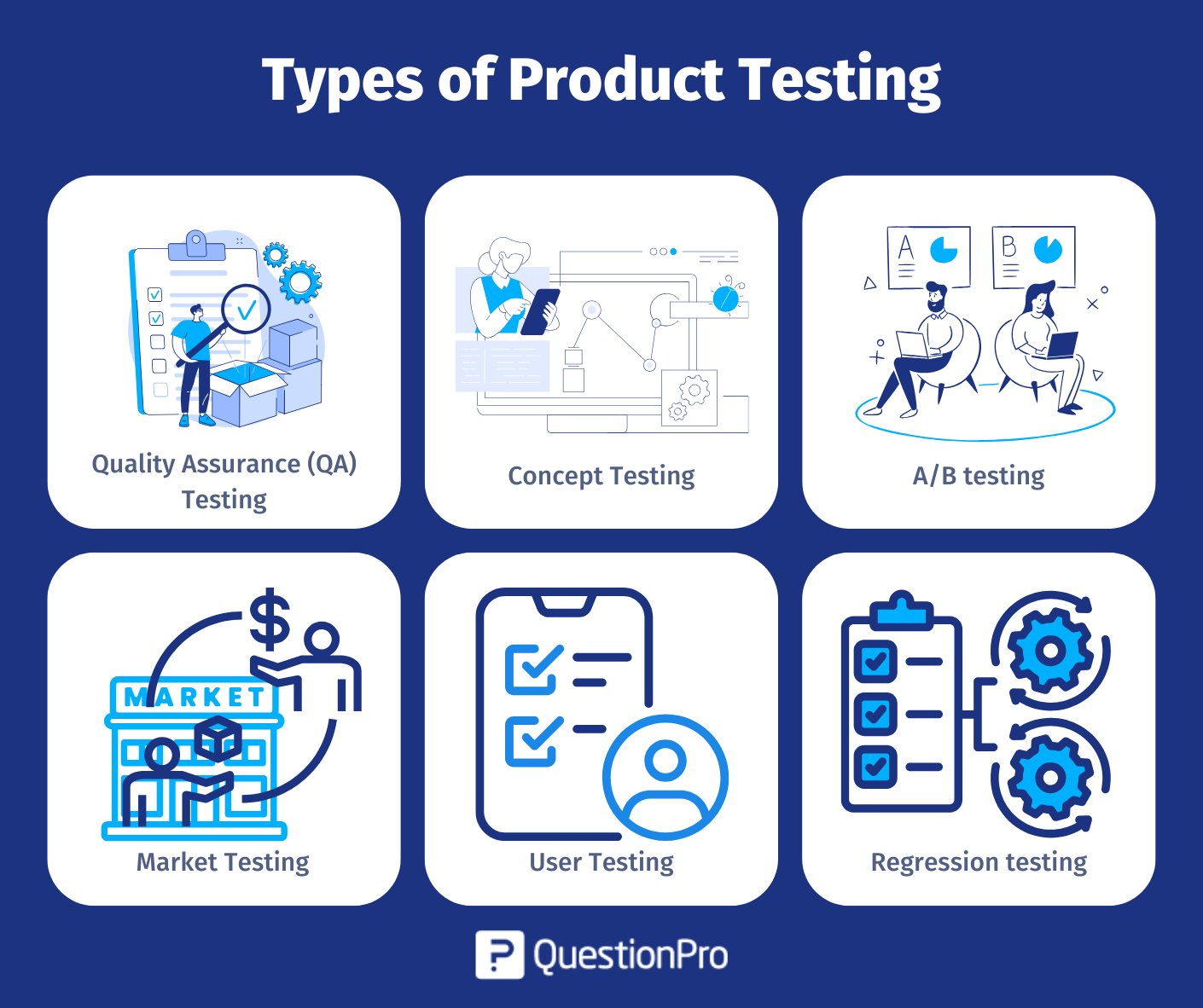
1. Quality assurance (QA) testing
QA testing is often done in a staged environment, where teams can test a product’s features or how it works before putting it out to the public. Most of the time, such teams evaluate a product by acting out different customer scenarios.
They might also use QA testing to check a product’s updates or new features before releasing them to the public. This kind of testing ensures the product works as planned and helps teams find problems before the product is released.
2. Concept testing
Product teams do concept testing to determine the sustainability of a product’s idea or concept and its potential market research companies value. It involves presentations, consumer surveys, wireframes, and frameworks for digital products like a website.
Concept testing can assist teams in deciding whether to continue development by examining client responses. It can also clarify product features or functions.
If you're interested in this type of testing, we recommend visiting our examples of Product Concept Tests.
3. A/B testing
Teams develop two versions of a product feature or component and ask customers which version they prefer in this testing. The differences between versions can be minor, such as two different color schemes for a website, or significant, such as two different product names.
Teams frequently use A/B testing to make design decisions based on customer preferences. It can also assist teams in learning more about their client’s requirements and preferences to build products that satisfy those expectations.
4. Market Testing
Market testing involves introducing a product to a small target market segment to its acceptance and performance before a full-scale launch. This type of testing helps businesses gather real-world data about how the product is received, identify potential issues, and understand customer feedback.
Businesses can use various methods for market testing, including pilot launches, focus groups, or pre-orders. The insights gained from market testing can inform adjustments to pricing, marketing strategies, and product features to increase the chances of success upon wider release.
5. User Testing
User testing focuses on evaluating the product from the end-user’s perspective. This method typically involves observing real users as they interact with the product, allowing teams to identify usability issues and areas for improvement.
User testing can take place in various formats, such as in-person sessions or remote testing. The goal is to gather feedback on the product’s functionality, ease of use, and overall user experience, ensuring it meets the needs and expectations of its intended audience.
6. Regression testing
This type of testing is done after customers have started using the product. During regression testing, teams test a product’s current features to determine which ones they want to add or change.
Some of the existing features stay the same, but regression testing helps teams determine if the new features change how the product works or how easy it is to use. Teams can test regression analysis to ensure the product works as expected after the update.
Product Testing Methods
Product testing methods vary based on the type of product, target audience, and specific objectives. Here are some effective methods you can utilize during the this phase:
Focus Groups
Focus groups bring together a small group of potential customers to discuss their thoughts on a product. This qualitative approach allows for deeper insights into customer attitudes, preferences, and potential improvements. Facilitators can guide discussions to cover various aspects of the product, such as
- Design,
- Functionality and
- Pricing.
Usability Testing
Usability testing evaluates how easy and user-friendly a product is. This method typically involves observing real users interacting with the product to identify any usability issues. It’s particularly useful for digital products, where the user experience is crucial to success.
Field Testing
In field testing, products are tested in real-world conditions by actual users. This method helps identify any practical issues that may not have been apparent in controlled environments. Gathering feedback during field tests can provide insights into how the product performs outside the lab.
Pilot Testing
Pilot testing involves releasing a product to a limited audience before a full-scale launch. This allows businesses to assess the product’s performance, gather feedback, and make necessary adjustments based on real user interactions.
Product Testing Process
This process typically involves several key steps to ensure the product meets the desired quality standards before release:
- Define Objectives: Determine what you want to achieve with the testing. Are you looking to validate a concept, assess usability, or gauge market interest?
- Select Methodology: Choose the appropriate testing methods based on your objectives, product type, and target audience.
- Recruit Participants: Identify and recruit participants who match your target audience for meaningful feedback.
- Conduct Testing: Execute the chosen testing methods, ensuring you gather both qualitative and quantitative data.
- Analyze Results: Review the data collected to identify trends, insights, and areas for improvement.
- Iterate: Use the feedback to make necessary changes to your product before finalizing the launch.
Product Testing vs. Concept Testing
Here’s a simple and relatable way to understand the differences between Product Testing and Concept Testing:
| Topic | Product Testing | Concept Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | It’s all about testing the actual product to see how it performs, feels, and meets expectations. | Focuses on exploring whether an idea or concept is worth pursuing. |
| When It Happens | Happens when a product is nearly finished or fully developed. | Happens early, when the idea is still just a concept or sketch. |
| What It Looks At | Checks real-world functionality, ease of use, and how much users like it. | Gauges consumer interest, potential value, and if it’s a good fit for the market. |
| How It’s Done | Involves testing prototypes, gathering feedback in focus groups, or letting users try it out. | Uses surveys, concept boards, or conversations to understand reactions to the idea. |
| Why It’s Useful | Helps improve features or confirm the product is ready to launch. | Decides if the idea is worth developing into a real product. |
| Example | Testing how well a new smartphone’s battery performs under daily use. | Asking people how they feel about a new smartphone concept with unique features. |
| Cost | More expensive because it involves creating prototypes or finished products. | Cheaper since you’re working with ideas or simple visuals. |
| Risk | Lower-risk changes are usually tweaks to an existing product. | Higher risk if the concept flops after heavy investment. |
Product Pricing and Product Testing
Here’s how Product Pricing and Product Testing differ, explained in a straightforward way:
Product Pricing
This is all about figuring out the sweet spot for your product’s price and what people are willing to pay while keeping profits in check.
- Goal: Find the perfect balance between what it costs to make, its value, and how it stacks up against competitors.
- How it’s done: Dive into market research, check out what competitors charge, and ask potential customers what they’d pay.
- Example: Deciding if that new smartphone should cost $1,000 or if $899 would bring in more buyers.
Product Testing
This step ensures your product does what it should and delights customers.
- Goal: Spot and fix any flaws, polish the product and make sure it’s market-ready.
- How it’s done: Test it out in real-life scenarios, gather feedback from focus groups, and run trials to see how it performs.
- Example: Seeing if the smartphone’s battery can last a day or if it survives a drop test.
Why They Go Hand-in-Hand
Product testing makes sure the product is worth buying, and pricing makes sure it’s worth selling. Together, they set the stage for a successful launch!
Learn more about Product Testing and Product Tester
Tips and Tricks for Product Testing
Consider using the best product testing sites available to ensure your product meets market demands. The following tips regarding testing will benefit your team during the product development process.
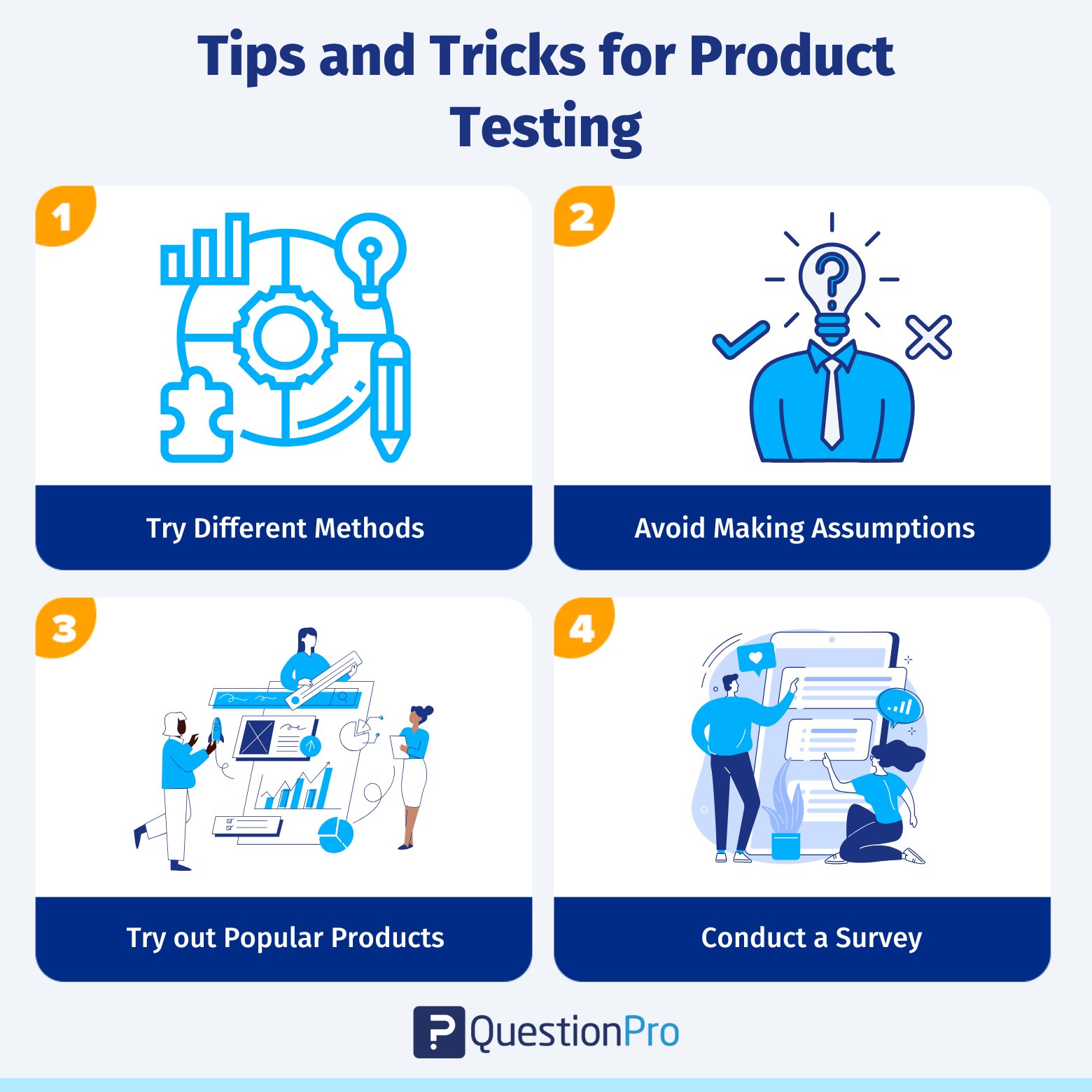
Try different methods
Using different ways to test a product helps to give clear direction during all stages of development. For example, your team might use concept testing to see if a product idea is good, QA testing to ensure it works as expected, and A/B testing to see how it looks.
Avoid making assumptions
It’s good to have a hypothesis before conducting this, but it could be a better idea to make assumptions about how customers will use or respond to the product. With such a frame of mind, you may analyze information dispassionately and make truly beneficial choices for your clients.
Try out popular products
It’s important to test products to find problems or risks, but it’s also helpful to try products that are already doing well to learn what’s already working well. Collect this information through testing and use it to make better products in the future.
Conduct a survey
A survey is a great way to get honest, helpful customer and target audience feedback about your product. It lets you develop products that meet your customers’ needs.
Mistakes to Avoid When Product Testing
While product testing is essential for success, there are common pitfalls to avoid:
- Neglecting Diverse Feedback: Relying solely on a small group of testers can lead to biased results. Ensure you gather feedback from a diverse audience to capture various perspectives.
- Ignoring Negative Feedback: Avoid dismissing negative feedback as irrelevant. Constructive criticism can provide valuable insights into areas for improvement that may not be immediately obvious.
- Overcomplicating the Testing Process: Keep the testing process straightforward and focused. Overly complicated methods can confuse participants and yield inconclusive results.
- Failing to Act on Feedback: Gathering feedback is only useful if you take action on it. Ensure that you implement necessary changes based on the insights gathered during testing.
- Not Testing Early and Often: Delaying this testing until the final stages of development can lead to costly mistakes. Start testing early in the products life cycle and continue iterating based on user feedback.
Start Improving your Product Testing with QuestionPro
In our discussion, we explored product testing, why it’s important, methods, and processes, and shared various tips and types of testing you can use. This is the key to meeting user needs, hitting business goals, and keeping the product team focused on the right projects.
No matter what method you choose, testing should be a part of the product life cycle. Because it is the best way to see how well your product ideas, functions, and changes work. You can use consumer testing methods to design, build, and market your new product, prototype, or feature to have the best chance of success.
A customer survey is a valuable tool for getting feedback from users. You may discover which product ideas are the most popular with customers by conducting product surveys and comparing variables like purchase intent, quality, and value.
With QuestionPro, you can speed up your product development cycle by putting all of your experience data on one platform. You can also quickly find gaps in the market and launch new products.







