
Quota sampling is a versatile non-probability sampling method designed to ensure that specific subgroups within a population are adequately represented in a study. Unlike probability sampling methods, which rely on random selection, quota sampling allows researchers to create samples based on predetermined characteristics such as age, gender, or occupation.
This approach can be handy when researchers need to gather insights from diverse groups efficiently. By setting quotas for each subgroup, researchers can achieve a balance that reflects the broader population, making it easier to analyze and generalize findings.
Did you know quota sampling is one of the most cost-effective ways to gather insights from specific population subgroups? It doesn’t matter if you are an independent researcher or part of a large company; this method can save you time and money.
In this article, we’ll explore the definition, types, steps, and practical examples of quota sampling to help you apply it effectively in your projects.
What is Quota Sampling?
Quota sampling is a non-probability sampling method in which researchers create a convenience sample of individuals representing a population and choose these individuals according to specific traits or qualities.
They decide and create quotas so that the market research samples can help collect data. These samples can be generalized to the entire population. The final subset will be decided only according to the interviewer’s or researcher’s knowledge of the population.
For example, a cigarette company wants to find out which age group prefers which brand of cigarettes in a particular city. They apply a survey quota to the age groups of 21-30, 31-40, 41-50, and 51+. The researcher gauges the smoking trend among the city’s population from this information.
Characteristics of Quota Sampling
Quota sampling has unique characteristics that distinguish it from other sampling methods. These attributes make it a valuable approach for researchers looking to gain insights into specific groups within a population. Below, we highlight the most notable characteristics of quota sampling:

- Aims to get the best representation of respondents in the final sample.
- Quotas replicate the population of interest in a real sense.
- The estimates produced are more representative.
- The quality of quota samples varies.
- It saves research data collection time as the sample represents the population.
- It saves research costs if the quotas accurately represent the population.
- It monitors the number of types of individuals who take the survey.
- The researcher always divides the population into subgroups.
- The sample represents the entire population.
- Researchers use the sampling method to identify the traits of a specific group of people.
These characteristics highlight why quota sampling can be a powerful tool in research. It offers unique advantages that enhance the quality and efficiency of data collection.
Types of Quota Sampling
Quota sampling is a non-probability sampling method that can be divided into two main types: controlled and uncontrolled. Each type has its own way of managing the sample:
Controlled Quota Sampling
In controlled quota sampling, the researcher sets specific criteria and limitations for selecting participants to ensure that the sample reflects certain predefined characteristics or proportions. This method involves:
- Predefined Criteria: The researcher determines specific quotas for different subgroups within the population, such as age, gender, or occupation. For instance, if a study aims to include 40% males and 60% females, the researcher will strive to meet these proportions precisely.
- Sample Selection: Researchers should strictly follow these quotas while choosing participants. This means they must actively seek out and include individuals who meet the criteria until the quotas are filled.
- Objective: The goal of controlled quota sampling is to ensure that the sample accurately represents the characteristics of the population, thereby enhancing the study’s generalizability and validity.
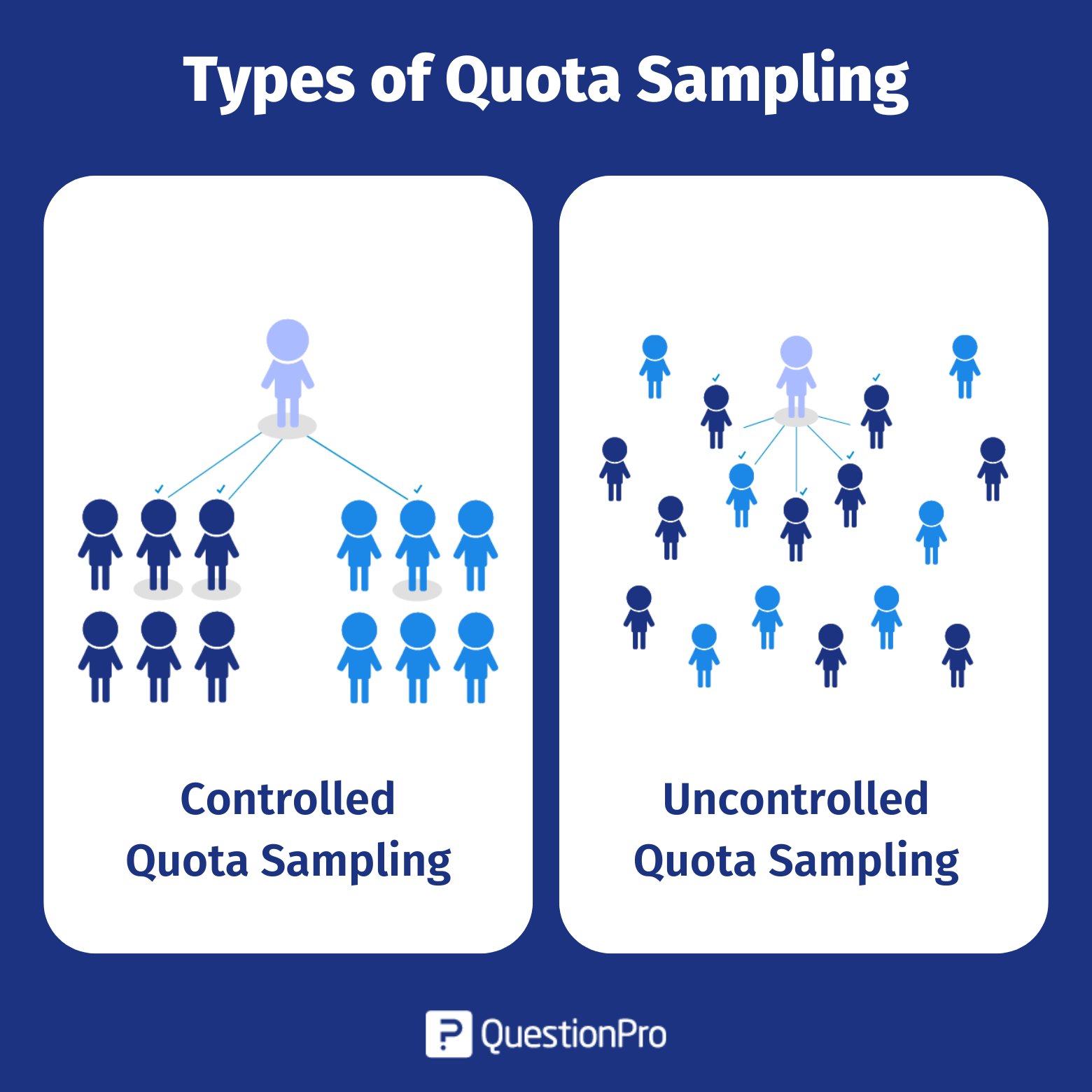
Uncontrolled Quota Sampling
Uncontrolled quota sampling, in contrast, does not impose specific constraints or restrictions on the selection process. This approach involves:
- Flexible Selection: Researchers have more freedom in choosing participants without depending on specific quotas or predefined characteristics. They can select participants based on convenience or availability if they reach a certain sample size.
- Less Restriction: Maintaining a proportionate representation of different subgroups within the sample is not required. This means that the sample may not accurately reflect the distribution of the population’s characteristics.
- Objective: The primary aim here is to quickly gather sufficient responses or participants rather than ensure a precise representation of all subgroups.
Controlled this is more structured and aims for precise representation according to predefined criteria. In contrast, uncontrolled quota sampling offers greater flexibility and focuses on achieving a sample size without specific demographic constraints.
What is the Difference Between Quota Sampling and Convenience Sampling?
When conducting research, choosing the right sampling method is crucial for obtaining reliable and representative data. Two common non-probability sampling techniques are quota sampling and convenience sampling. Understanding the differences between these methods can help researchers select the most suitable approach for their study objectives.
| Topic | Quota Sampling | Convenience Sampling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A method where researchers ensure specific subgroups are represented based on predetermined quotas. | A method where researchers select participants based on their easy availability and willingness to participate. |
| Selection Process | Participants are chosen based on specific characteristics to meet set quotas. | Participants are chosen simply because they are accessible, without regard for representativeness. |
| Representativeness | Can be biased if the quotas are not carefully defined or the selection process is flawed. | Often, it lacks representativeness as it fails to ensure that different subgroups are adequately included. |
| Bias Potential | Can be biased if the quotas are carefully defined or the selection process needs to be revised. | Highly susceptible to bias, as the sample may not reflect the broader population due to reliance on convenience. |
| Data Collection Efficiency | May require more time and effort to ensure quotas are filled appropriately. | Quick and easy to conduct, as it relies on readily available participants. |
| Common Use Cases | Used when specific subgroup representation is essential, such as in market research. | Often used in preliminary research, pilot studies, or when time and resources are limited. |
How to Perform Quota Sampling?
Probability sampling techniques involve many rules the researcher must follow to form samples. But, since quota sampling is a non-probability sampling technique, there are no rules for formally creating samples. Usually, there are four steps to form a quota sample. Here are the steps:
- Divide the sample population into subgroups: With stratified random sampling, the researcher bifurcates the entire population into mutually exhaustive subgroups, i.e., the elements of each subgroup become a part of only one of those subgroups. Here, the researcher applies random selection.
- Figure out the weightage of subgroups: The researcher evaluates the proportion of the population in which the subgroups exist. He/she maintains this proportion in the sample selected using this sampling method. Subgroup analysis is crucial for tailoring treatments to specific patient groups and optimizing healthcare outcomes.
For example, 58% of the people interested in purchasing your Bluetooth headphones are between 25 and 35. In that case, your subgroups should also have the same percentage of people in the respective age group. - Select an appropriate sample size: In the third step, the researcher should select the sample size while maintaining the proportion evaluated in the previous step. For example, if the population is 500, the researcher can pick a sample of 50 elements.
The sample chosen after following the first three steps should represent the target population. - Conduct surveys according to the defined quotas: To achieve actionable results, stick to the predefined quotas. Don’t survey full quotas; focus on completing surveys for each quota.
Applications of Quota Sampling
Below are the instances where quota sampling is applied and used.
- In situations where researchers have specific criteria for conducting research, this allows the selection of subgroups, which makes it extremely convenient for researchers to obtain desired results. A trait or characteristic can be the filter for subgroup formation.
- The researcher uses this method when he/she has time constraints. Applying quotas gives the researcher an idea of the population of interest in very little time.
- Quotas are applied when the researcher is on a tight budget. Instead of researching a large population, the researcher saves money by using a few quotas to get the whole picture of the population.
- Due to the nature of the research project, some studies do not require pinpoint accuracy. Therefore, it is ideal to apply quota sampling to these studies.
Advantages of Quota Sampling
Here are the top four advantages of quota sampling:
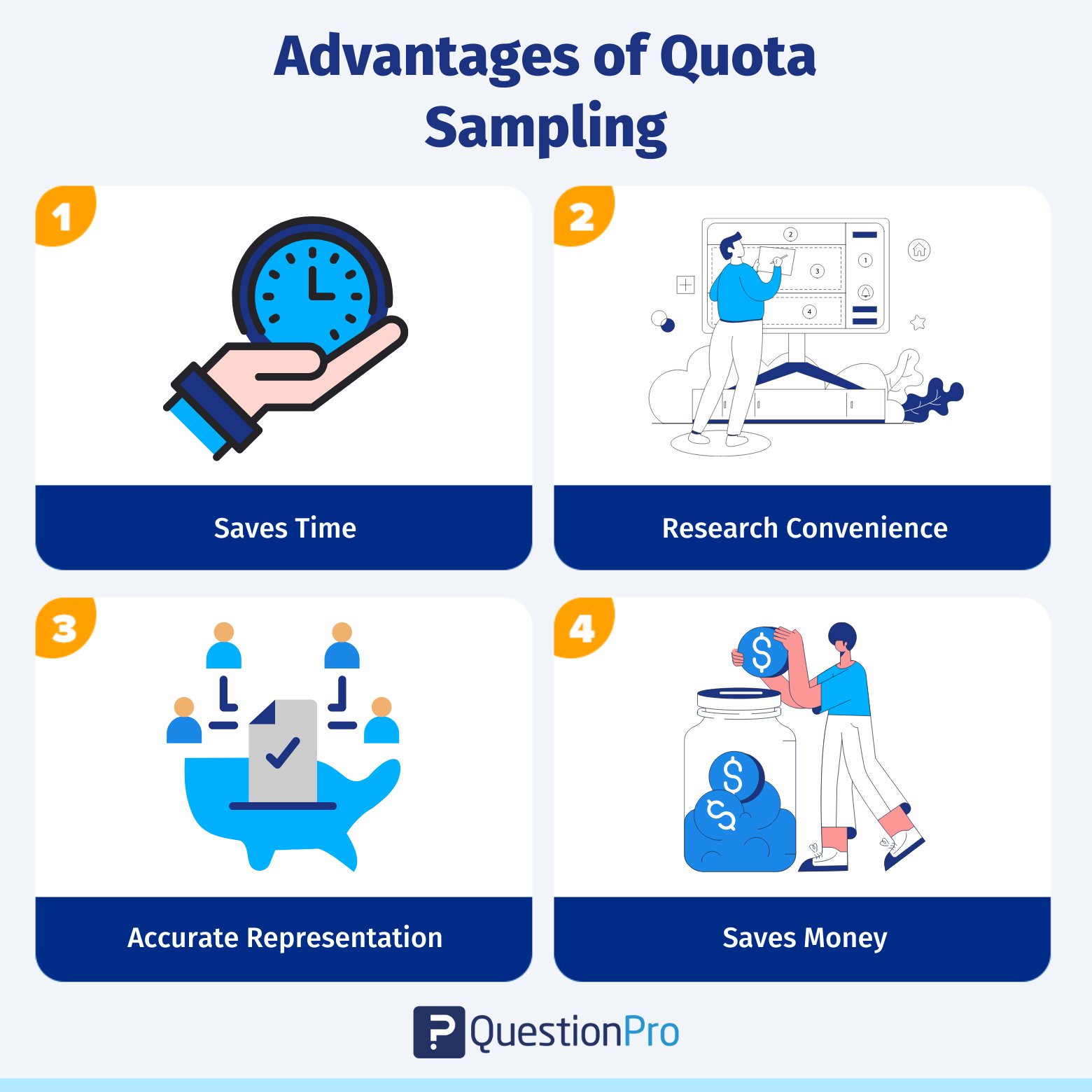
- Saves time: This sampling process is quick and straightforward because a quota is involved in sample creation.
- Research convenience: By using quota sampling and appropriate research questions, researchers can interpret information and responses to the survey much more conveniently.
- Accurate representation of the population of interest: Researchers effectively represent a population using this sampling technique. There is no room for over-representation as this sampling technique helps researchers to study the population using specific quotas.
- Saves money: The budget required for executing this sampling method is minimalistic.
Quota Sampling Example
To better understand the concept of Quota Sampling, let’s explore the following scenario as an example:
A researcher wants to survey individuals about what smartphone brand they prefer to use. He/she considers a sample size of 500 respondents. Also, he/she is only interested in surveying ten states in the US. Here’s how the researcher can divide the population by quotas:
- Gender: 250 males and 250 females
- Age: 100 respondents each between the ages of 16-20, 21-30, 31-40, 41-50, and 51+
- Employment status: 350 employed and 150 unemployed people.
- (Researchers apply further nested quotas. For example, out of the 150 unemployed, 100 must be students.)
- Location: 50 responses per state
Depending on the type of research, the researcher can apply quotas based on the sampling frame. The researcher doesn’t need to divide the quotas equally. He/she divides the quotas according to his/her needs (as shown in the example where the researcher interviews 350 employed and only 150 unemployed individuals). Random sampling can be conducted to reach out to the respondents.
Use our free tool to start calculating your sample size; no complex math—just enter your population, confidence level, and margin of error, and you’re ready! Visit our Free Sample Calculator.
Quota Sampling with QuestionPro Audience
QuestionPro Audience offers access to a diverse pool of over 22 million survey respondents worldwide, making it an ideal platform for conducting quota sampling. Whether you need to apply hard quotas to your survey or target specific niche audiences, QuestionPro Audience provides the tools to ensure that your sampling process is efficient and precise.
With this platform, researchers can set quotas based on demographics such as age, gender, location, employment status, and more, ensuring that their sample accurately reflects the characteristics of their target population.
QuestionPro Audience can help reach the right respondents quickly for studies requiring specific subgroup representation. The platform allows researchers to define strict quotas and select from a global panel to meet those requirements, leading to more reliable and actionable insights.
Additionally, QuestionPro Audience’s extensive reach makes finding niche or hard-to-reach participants easy, regardless of the study’s complexity or scope.
Conclusion
Quota sampling offers a practical solution for researchers who can quickly gather data from specific population segments while adhering to certain characteristics. This controlled or uncontrolled method allows for flexibility and efficiency in data collection.
While it may provide a different level of precision than probability sampling methods, its time and cost savings advantages make it a valuable tool for various research scenarios. By correctly understanding and implementing quota sampling, researchers can ensure their samples accurately represent their target groups and derive meaningful insights from their studies.
By utilizing QuestionPro Audience, businesses, and researchers can streamline their data collection processes, saving time and resources while ensuring high-quality results. Whether your project involves complex quotas or niche audiences, QuestionPro Audience provides the flexibility and expertise to meet your research objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A: Yes, but it requires careful planning to ensure subgroups are accurately represented.
A: Quota sampling relies on non-random selection to fill quotas, while stratified sampling involves random selection from predefined strata or subgroups.
A: Yes, quota sampling can be biased due to the non-random selection process, which may not accurately reflect the population.
A: Quota sampling is best used when researchers need to quickly gather data from specific subgroups and ensure their representation within a study.







