
Unmoderated testing offers a dynamic approach to user research and usability testing, presenting numerous advantages and unique challenges. This method is known for being more cost-effective, faster, and readily accessible compared to moderated or in-person research, which is why it’s favored by many.
Unmoderated usability testing has completely transformed how you gain valuable insights into the user experience of websites, applications, and products as a researcher or UX professional. With this innovative approach, you can let users interact with digital interfaces without needing a moderator right beside them, allowing you to observe their natural behaviors and interactions.
In this blog, we will delve into the purpose, advantages, challenges, and best practices of unmoderated testing, shedding light on when and how to utilize this method effectively in your research endeavors.
What is Unmoderated Testing?
Unmoderated testing is a research method in which users or participants interact with a product, website, or application without a moderator or researcher’s direct presence or guidance. It involves assigning users predefined tasks and scenarios to complete and asking them to contribute their feedback, thoughts, and experiences while using the system.
The following are the main aspects of unmoderated tests:
- Remote Participation: Users can use the product from their own place and at their own time.
- Predefined Tasks: Users are given specific things to do to see how the product works like they would in real life.
- Limited Moderator Involvement: Unlike moderated testing, no moderator is present to guide or observe the user during the session. Participants navigate the system independently.
- User Feedback: Users are asked to share their thoughts in writing, video, or audio, explaining how they felt while using the product.
- Quantitative and Qualitative Data: Unmoderated usability testing provides quantitative data, such as task success rates and completion times, and qualitative insights into user behavior, challenges, and satisfaction.
- Scalability: It’s easier to do unmoderated usability testing with lots of people because we don’t need a moderator for each person. This is good for studies with many participants.
Purpose of Unmoderated Testing
The purpose of unmoderated testing is to gain valuable insights into the user experience of websites, applications, or digital products. It allows participants to interact with these interfaces in a natural, unsupervised manner, which provides a genuine user perspective.
Here’s why unmoderated usability testing is valuable for you:
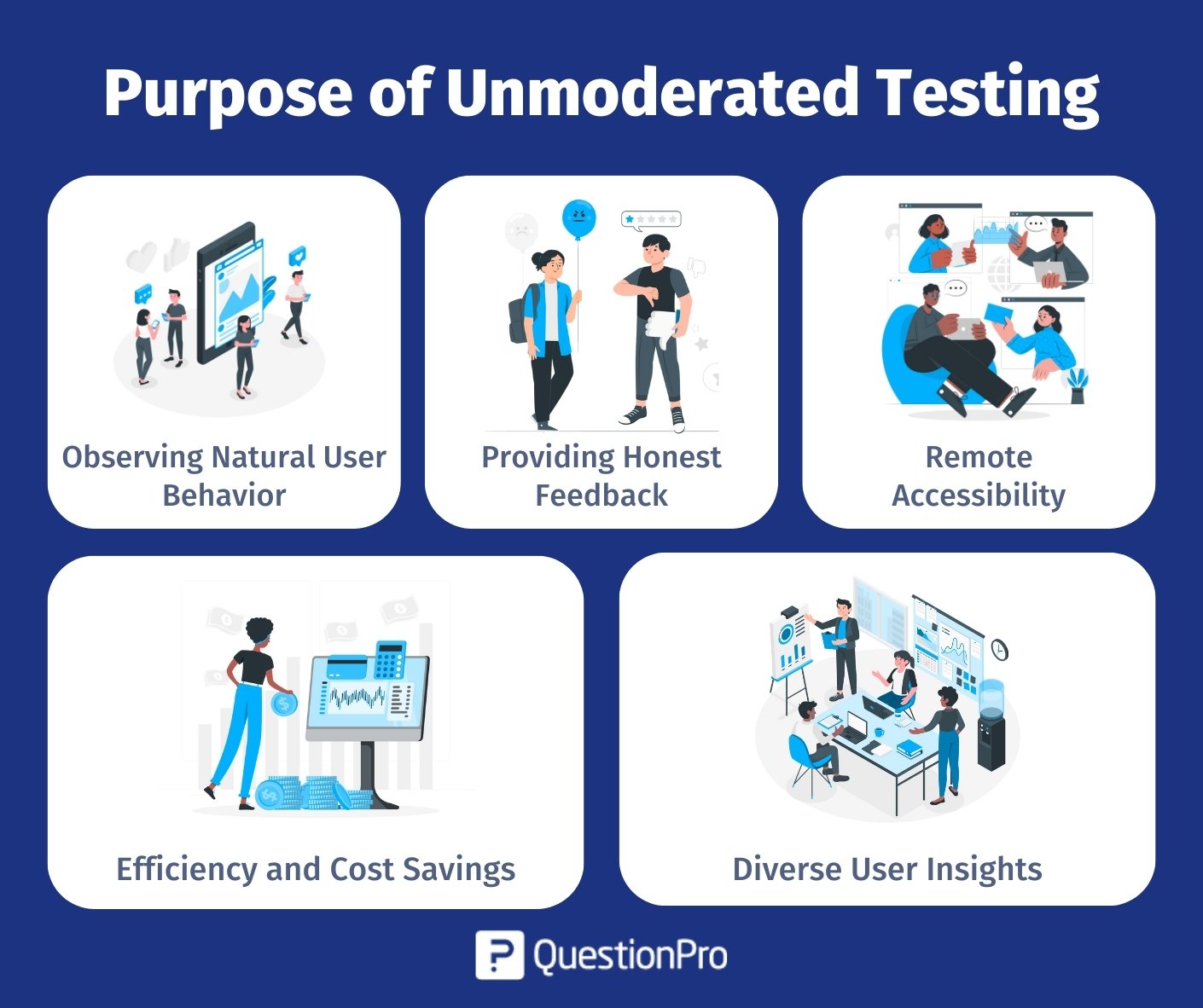
Observing Natural User Behavior
Unlike moderated usability testing, unmoderated usability testing lets participants engage with a product as you naturally would, without the presence of a moderator. This means your participants’ actions and reactions are more authentic, reflecting real-world usage.
Providing Honest Feedback
Your participants have the opportunity to provide candid and unbiased feedback since there’s no moderator influence. This helps researchers gather your unfiltered opinions about the product’s strengths and weaknesses.
Remote Accessibility
Unmoderated testing is accessible from any location, making it convenient no matter where you are. This accessibility is especially useful when researchers need a diverse set of participants.
Efficiency and Cost Savings
Unlike traditional moderated tests, unmoderated testing is more efficient and cost-effective. It can be done at your own pace, which saves time and resources.
Diverse User Insights
Your participation contributes to a diverse pool of insights. This diversity helps identify usability issues and preferences across different demographic groups.
Advantages of Unmoderated Testing
Unmoderated testing offers numerous advantages that make it a valuable method for user research and usability assessment. Here are some of the key benefits:
Flexibility and Convenience
Unmoderated tests offer you remarkable flexibility and convenience. It allows you to accommodate a wider range of participants’ schedules and time zones, which enables them to engage with your product or website at their own convenience.
This flexibility eliminates the need for synchronous sessions, making it easier to collect data from a diverse set of users. Participants can take the test when it suits their schedules best, without the pressure of setting appointment times, which is especially appealing for busy individuals.
Scalability
Scalability is a significant advantage that unmoderated usability testing brings to you as a researcher. It’s an efficient way to include a large number of participants in your study.
Whether you’re aiming to reach a broad audience or require extensive data for your research, unmoderated tests allow you to quickly scale up your efforts without a corresponding increase in resources or time. This makes it an ideal choice when you need to quickly gather insights from a considerable pool of users.
Cost-Effectiveness
Unmoderated testing represents a cost-effective alternative for you as a researcher. You’ll realize significant cost savings without the need for in-person facilitators or moderators.
Participants can also use their own devices and perform tasks remotely, which reduces expenses. For participants, this means a greater likelihood of being compensated for their time and effort, making it an attractive option for them to participate.
Diverse Participant Pools
Unmoderated usability testing brings the advantage of attracting a more diverse set of participants to your research. Since it can be conducted remotely, it is accessible to individuals from various geographic locations and backgrounds.
This diversity can be a significant asset, allowing you to gather insights from a broader range of users. It’s beneficial when you aim to understand how different user groups interact with a product or service.
Challenges of Unmoderated Testing
While unmoderated testing has many advantages, it also has its own set of challenges and limitations. Understanding these challenges is essential for researchers making informed judgments regarding when and how to utilize unmoderated tests. The following are the primary challenges with unmoderated usability tests:
Lack of Real-Time Guidance
One of the primary challenges you face in unmoderated usability testing is the absence of real-time guidance. Participants may encounter difficulties or questions during the testing process without a moderator present to provide immediate assistance.
This lack of support can potentially affect their experience and the data quality, making it crucial for you to design tasks and instructions to mitigate this challenge carefully.
Participant Motivation
Maintaining participant motivation and engagement in unmoderated usability tests can be another significant challenge for you. Participants may be more prone to distractions or disengagement without a moderator’s encouragement and guidance.
Ensuring Data Quality
Ensuring data quality is a paramount concern in usability testing. Without a moderator present to verify task completion and provide immediate feedback, you must implement robust data collection methods.
It’s essential that participants provide accurate, detailed, and honest feedback to contribute to the overall quality of your research. You may need to implement additional checks and validations to maintain data integrity.
When to Use Unmoderated Usability Testing?
Unmoderated usability testing is a valuable method that finds its strength in specific scenarios where efficiency, diversity, and real-world user behavior are paramount. Here’s when you should consider using unmoderated usability tests:
- Large Sample Size: When you need to gather insights from a substantial and diverse group of contributors, unmoderated usability testing shines. It enables you to reach a broad spectrum of users, making it ideal for projects that require a significant sample size.
- Quick Feedback: Unmoderated usability tests are the go-to choice when time is of the essence. If you need rapid feedback on your concept, design, or product, this method allows you to collect data swiftly, saving precious time in your research process.
- Natural Environment Interaction: Unmoderated usability testing excels at capturing user interactions in their natural environment. If you want to see how contributors engage with your product without external influences, this method provides an authentic representation of real-world user experiences.
- Limited Moderation Resources: In cases where you are constrained by time or lack the resources to moderate a test, unmoderated usability testing is a practical solution. It allows you to conduct usability testing without needing a dedicated moderator, making it a cost-effective option.
Depending on your project requirements, unmoderated usability testing can be particularly beneficial in the following situations:
- Evaluating Websites or Apps: Unmoderated testing is especially useful when assessing live websites or recently launched applications. It provides real-time user feedback, helping you identify issues and areas for improvement quickly.
- Assessing Prototypes: If you have a website or app prototype and want to test its viability, unmoderated tests are convenient. Participants can interact with your prototype, offering insights into its usability and potential issues.
- Ethnographic Studies: Unmoderated usability testing can also be valuable for conducting ethnographic studies. This approach allows you to observe real-world user experiences, such as unboxing a product, in an unscripted and natural setting.
How to Conduct Remote Unmoderated Testing?
Remote unmoderated tests involve several key steps to ensure a successful research process. Here is how you can conduct remote unmoderated usability testing:
- Define Research Objectives and Scope: Begin by clearly defining the objectives of your unmoderated usability testing. Determine what aspects of the user experience you want to evaluate and set specific research goals.
- Select a Usability Testing Tool or Platform: Choose a suitable unmoderated testing tool or platform. Ensure the platform aligns with your research needs and provides the required features.
- Create User Scenarios and Tasks: Develop a set of user scenarios and tasks that participants will undertake during the testing.
- Participant Recruitment: Utilize the capabilities of your chosen testing platform to recruit test participants. Specify the demographic characteristics and user profiles you are looking for to ensure that you reach your target audience.
- Prepare Instructions: Craft clear and concise instructions for participants. Provide an overview of the study’s purpose, explain how to use the testing tool, and offer specific guidance on how to complete the tasks.
- Launch Testing Sessions: Run the usability tests. Participants access the unmoderated usability testing platform and follow the instructions. They complete the assigned tasks by providing feedback through written responses, audio recordings, or video recordings.
- Data Collection: The testing platform collects data as participants engage with the tasks. This data includes quantitative metrics, such as task success rates and time on task, and qualitative data, such as participant comments and feedback.
- Analyze The Results: Analyze the collected data to draw insights. Look for patterns, trends, and user behavior that align with your research objectives.
Data Collection in Unmoderated Usability Testing
Unmoderated usability testing offers a variety of data collection methods to capture user behavior, feedback, and insights. These methods enable researchers to understand the user experience and product usability comprehensively. Here are the primary data collection methods used during unmoderated tests:
01. Screen and Interaction Recording
Unmoderated testing tools often include screen and interaction recording capabilities. This method captures the participant’s screen activity, including mouse movements, clicks, and page navigation.
It provides a visual record of the user’s journey through the product, helping researchers identify specific areas where users encounter issues or confusion.
02. Participant Comments and Feedback
Structured surveys or questionnaires are the best ways to collect user self-reported data. During the testing session, participants can provide real-time comments and feedback.
Participants can type text-based comments, voice their thoughts, or provide feedback through audio or video recordings. This qualitative data offers insights into the participant’s thought process and user experience.
03. System Usability Scale (SUS)
The System Usability Scale is a standardized questionnaire that participants can complete after their testing session. It assesses the overall usability and user satisfaction of a product.
04. Clickstream and Heatmaps
Some unmoderated testing tools generate clickstream data, which records the sequence of clicks and interactions during the session.
Heatmaps visualize areas of interest and interaction frequency on the website or app, helping researchers identify where users focus their attention and activity.
05. Emotion and Satisfaction Metrics
Some platforms incorporate metrics related to user emotions and satisfaction. Participants can be asked to rate their emotional state during the session, providing insights into user sentiment.
Post-session surveys can capture participant satisfaction and overall experience feedback.
06. Participant Self-Reflection
After completing tasks, participants may be asked to reflect on their experience or suggest improvements. These self-reflection components offer valuable qualitative data, allowing participants to express their thoughts and ideas.
Best Practices to Conduct Unmoderated Testing
Unmoderated testing is a powerful method for gaining user insights, but it requires careful planning and execution to yield meaningful results. Here are some best practices to ensure a successful unmoderated usability testing process:
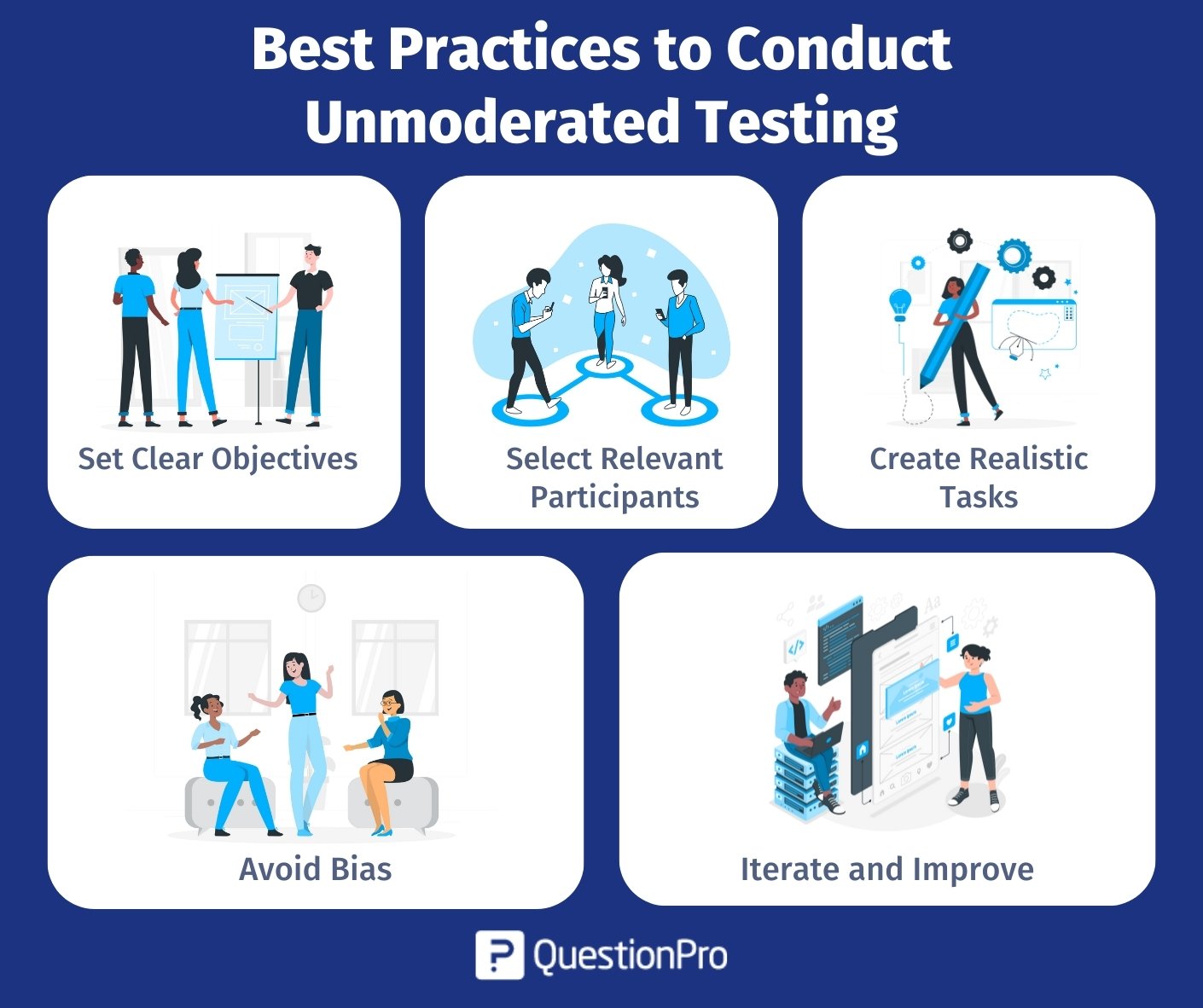
- Set Clear Objectives: Clearly set your research goals and questions. What are you trying to achieve? What research questions do you want to answer? This clarity will guide the entire process.
- Select Relevant Participants: Ensure you recruit participants matching your target audience and user personas. The quality of your participant pool is crucial for obtaining relevant and actionable feedback.
- Create Realistic Tasks: Develop user scenarios and tasks that closely resemble real-world interactions with your product. Tasks should be specific, realistic, and relevant to your research objectives.
- Avoid Bias: Avoid leading questions that might bias participants’ responses. Keep questions neutral and open-ended.
- Iterate and Improve: If your unmoderated testing reveals significant usability problems, consider implementing design or functionality changes and conduct further testing to assess the impact of these improvements.
The Role of QusestionPro in Unmoderated Testing
QuestionPro is a versatile online survey and research platform that can play a valuable role in unmoderated usability testing. Here are some ways in which QuestionPro can be used in unmoderated tests:
- Participant Recruitment: QuestionPro can be used to recruit test participants for unmoderated usability testing studies. You can create screening surveys to identify participants who match your audience, ensuring that you have the right users for your study.
- Task Scenario Presentation: You can use QuestionPro to present participants with task scenarios and instructions. These can be designed as surveys or forms, guiding participants through the tasks and collecting their responses.
- Data Collection: QuestionPro allows you to gather data from unmoderated usability test sessions through various question types. You can create surveys with multiple-choice questions, open-ended questions, rating scales, and more to capture both quantitative and qualitative data.
- Emotion and Satisfaction Metrics: You can incorporate standardized scales and questionnaires, such as the System Usability Scale (SUS), to assess participants’ user experience and satisfaction after completing their unmoderated test sessions.
- Participant Feedback: Use open-ended questions to collect participant feedback and comments during or after the unmoderated testing tasks. Participants can share their thoughts and suggestions in text format.
- Demographic and Background Information: QuestionPro can collect demographic and background information about participants, helping you segment and analyze results based on user profiles.
- Analytics and Reporting: QuestionPro provides analytics tools and reporting features, allowing you to analyze the collected data during unmoderated tests and generate reports to share with stakeholders.
- Integration with Data Analysis Tools: You can export data collected through QuestionPro for further analysis using data analysis tools or software, helping you delve deeper into the insights gathered from unmoderated tests.
By incorporating QuestionPro into your unmoderated testing process, you can streamline the overall process more efficiently and organized. This can help you gain valuable insights into the user experience and make data-driven decisions to enhance your products and services.
You can create a free account to try the tool or request a free demo to discuss your needs.







