Have you ever thought about how usability vs. user testing differs? People often use these two terms equally, but there is a big difference between them. Both have a goal, which is why they are alike. Both try to find problems with functions and UX design that hurt the user experience as a whole.
User testing vs usability testing is two distinct approaches to evaluating a product’s effectiveness and user experience, with user testing focusing on gathering feedback from users to understand their needs and preferences. While usability testing concentrates on assessing the product’s ease of use and efficiency.
Unsurprisingly, so many business owners, web designers, web developers, and digital marketers mix them up. So, in this blog, we’ll clarify the distinctions between user and usability testing and why both represent essential phases in understanding your users’ requirements.
What is usability testing?
Usability Testing, also called User Experience Testing (UX Testing), is a way to find out how user-friendly and easy to use a product or service is by looking at user feedback and ideas. In this testing method, a small group of people is chosen based on the characters created for the product or service. They are then asked questions about the product or service and asked to interact with it.
At the same time, a moderator takes notes or records the whole session so that they can later look at the participants’ concerns, pain points, and comments. Companies worldwide put a lot of money into this testing to reduce the chances of failure or loss in the long run or after the product or service is finally released.
Importance of usability testing
Usability testing is crucial for the success of any product or service that involves user interaction. It involves evaluating a product by testing it with representative users to identify usability issues and gather feedback. Here are some key reasons why usability testing is important:
User-Centric Design
Usability testing ensures that a product or service’s design aligns with its intended users’ needs, expectations, and behaviors. Involving users early in the development process helps create a user-centric design that caters to their preferences and enhances their overall experience.
Identify and Prioritize Issues
Website usability testing helps identify usability problems, pain points, and bottlenecks in a product’s user interface or interaction flow. By observing users in real-world scenarios, designers and developers can understand where users struggle, get confused, or encounter difficulties. This allows them to prioritize and address these issues before the product is released.
Improve User Satisfaction
Organizations can gain insights into user preferences and expectations by conducting usability testing. It helps refine the product’s design, layout, and features to meet user needs better, resulting in increased user satisfaction. When users find a product easy to use and navigate, it enhances their overall experience, increases trust, and encourages them to continue using the product or service.
Cost and Time Efficiency
Early identification and resolution of user issues through testing can save significant time and resources in the long run. By detecting and addressing problems early in the development process, organizations can avoid costly redesigns or redevelopments after the product is launched. Conducting usability tests helps optimize the product’s design and functionality, minimizing the risk of expensive fixes or negative user experiences later on.
Competitive Advantage
In today’s competitive market, providing a superior user experience is a key differentiator. Usability testing allows organizations to gain a competitive edge by better understanding user needs and preferences than their competitors. By delivering a product that is easy to use, efficient, and enjoyable, businesses can attract and retain more customers, leading to increased market share and brand loyalty.
Validation and Confidence
Usability test provides validation and confidence to product teams. Involving users in testing helps validate design decisions, ensuring that the product aligns with user expectations. This validation builds confidence among stakeholders, as decisions are based on real user feedback rather than assumptions or personal preferences.
What is user testing?
User testing tries to determine if a product or feature is needed by determining how your target audience uses and feels about it. Despite its name, user testing has little to do with the user experience (UX). Instead, user testing methods try to find out if the product’s intended people really need it and would be able to use it.
User testing is similar to user research in many ways. Using methods like focus groups and polls, you can find out more about your audience’s pain points, wants, behaviors, and more. Then, you can figure out if your idea solves a problem for a given test user and if there are enough people interested in the idea.
Importance of user testing
User testing is important for understanding and improving the user experience of a product or service. It involves observing and gathering feedback from real users as they interact with the product, allowing organizations to make informed decisions based on user needs and preferences. Here are some key reasons why user testing is important:
User-Centered Design
User testing ensures that a product’s design and functionality align with its target user’s actual needs and behaviors. Organizations can create intuitive, efficient, and satisfying products by involving users early in the design process and throughout the development cycle.
Uncover Usability Issues
It helps identify usability issues, pain points, and areas of improvement in a product’s design or functionality. By observing users firsthand, organizations can understand where users struggle, get confused, or encounter difficulties. This feedback enables designers and developers to address these issues, resulting in a more user-friendly product.
Validate Design Decisions
User testing provides validation for design decisions and helps teams make data-driven choices. By observing how users interact with a product, organizations can verify whether their design hypotheses and assumptions are accurate or need adjustment. This validation helps reduce the risk of creating a product that does not meet user needs or expectations.
Optimize User Experience
Through user acceptance testing, organizations can gather insights into user preferences, behaviors, and pain points. This information allows them to refine and optimize the user experience, making the product more enjoyable, efficient, and valuable for users. User testing helps uncover opportunities for improvement and innovation, leading to a better overall user experience.
Iterative Development
User tests facilitate an iterative development approach, where products are tested and refined in multiple cycles. Organizations can make incremental improvements and continuously enhance the product by incorporating user feedback into each iteration. This iterative process ensures that the final product is more robust, user-friendly, and aligned with user expectations.
Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty
User testing help create products that meet user needs and preferences, leading to higher customer satisfaction. When users have a positive experience with a product, they are more likely to become loyal customers, recommend the product to others, and provide positive reviews and feedback. User testing plays a critical role in building customer satisfaction and fostering long-term relationships with users.
Cost Savings
User testing can save organizations time and resources by identifying and resolving issues early in development. By detecting usability problems and addressing them before launch, organizations can avoid costly redesigns, redevelopments, or negative user experiences down the line. User testing helps mitigate risks and ensures that resources are allocated efficiently.
Differences between usability testing vs. user testing
Usability testing is often conducted in a controlled environment with specific tasks. In contrast, user testing aims to observe users in their natural environment, considering the overall user experience. Both types of testing involve representative users or target audiences. Still, usability testing emphasizes identifying and addressing the usability issue, while user testing explores user needs and expectations.
Here’s a table outlining the key differences between usability testing and user testing:
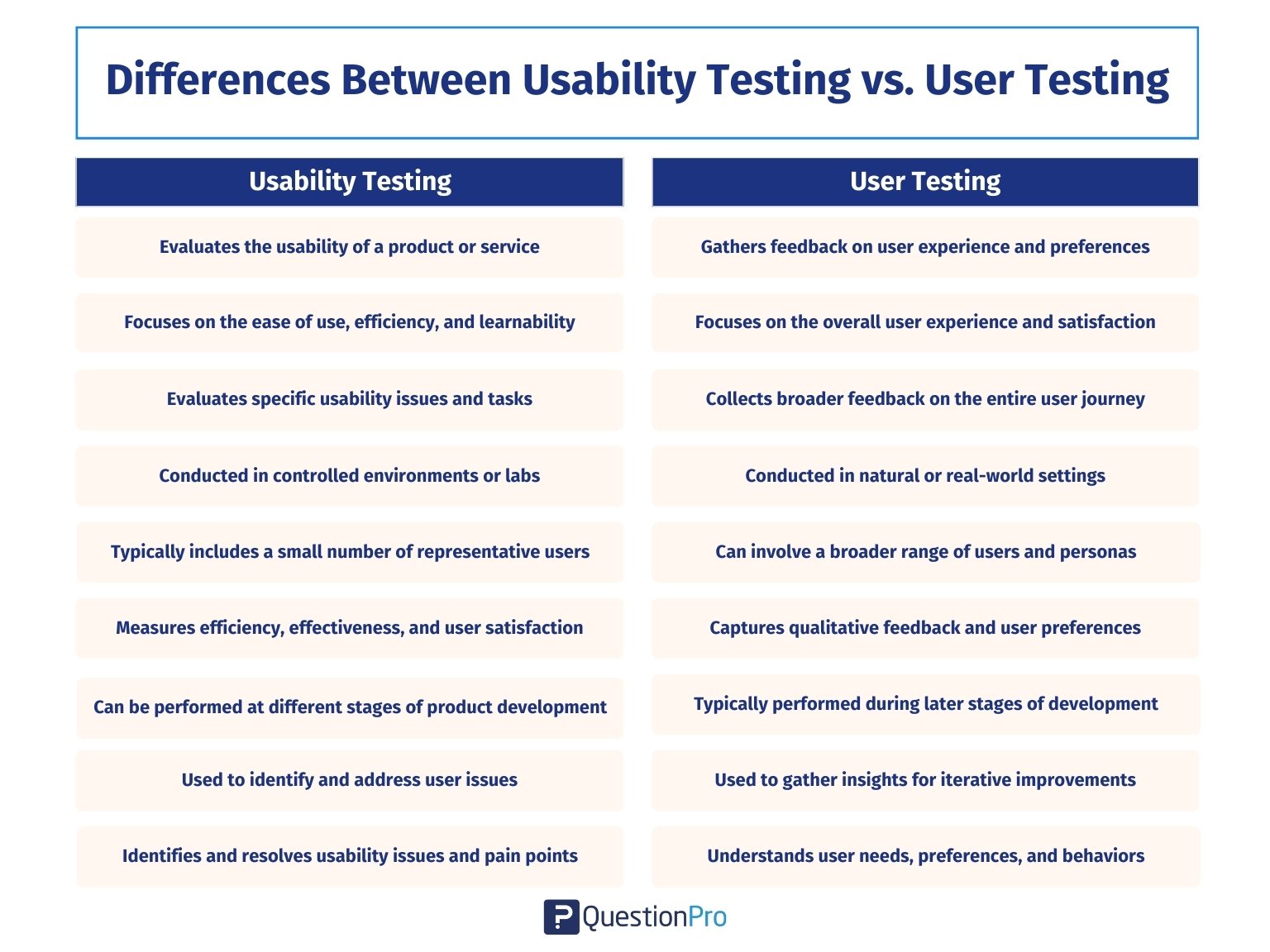
- Purpose:
Usability Testing: Evaluate the usability of a product or service.
User Testing: Gather feedback on user experience and preferences
- Focus:
Usability Testing: Focuses on the ease of use, efficiency, and learnability
User Testing: Focuses on the overall user experience and satisfaction
- Scope:
Usability Testing: Evaluates specific usability issues and tasks
User Testing: Collects broader feedback on the entire user journey
- Method:
Usability Testing: Conducted in controlled environments or labs
User Testing: Conducted in natural or real-world settings
- Participants:
Usability Testing: Typically includes a small number of representative users
User Testing: Can involve a broader range of users and personas
- Metrics:
Usability Testing: Measures efficiency, effectiveness, and user satisfaction
User Testing: Captures qualitative feedback and user preferences
- Timing:
Usability Testing: Can be performed at different stages of product development
User Testing: Typically performed during later stages of development
- Iteration and refinement:
Usability Testing: Used to identify and address user issues
User Testing: Used to gather insights for iterative improvements
- Goal:
Usability Testing: Identify and resolve usability issues and pain points
User Testing: Understand user needs, preferences, and behaviors
Conclusion
User and usability testing are important parts of making products and services work better. Usability testing looks at how easy something is to use and how well it works, while user testing looks at the general user experience and preferences.
In the case of QuestionPro survey software, usability testing would look at how well surveys are made and run. In contrast, user testing would look at the user interface, how surveys are filled out, and how satisfied people are with the software as a whole.
QuestionPro can improve its software to provide a user-friendly experience, ensuring ideal usability and user satisfaction, by incorporating both usability vs. user testing.







