
Have you ever thought that all the purchases we make involve a buying process before the time of the transaction? We call this process the customer journey, which encompasses all the phases a person/buyer persona goes through from the moment they identify their need until they acquire a product or service to satisfy it.
This process can be as short as a few minutes in the case of low-cost products that we buy impulsively (food in a supermarket, for example). The purchasing process may also last for months or more than a year (for instance, when acquiring a car or purchasing a customer experience management software).
This article will cover the customer journey, its phases, and how we can define it in our customer experience strategy.
Remember to download the free Customer Journey Map template at the end of this guide!
What is a Customer Journey?
The customer journey is the sequence of steps when interacting with a brand, from first hearing about it to purchasing and beyond. It includes every customer experience along the way, helping businesses understand how to improve each step for a smoother, more satisfying process.
The focus isn’t only on transactions and how the customer feels after every interaction with the brand. In other words, the customer journey can be used as a strategy to gain insights into the customer’s experience throughout their buying process.
The objective of these journeys is, on the one hand, to measure and evaluate how you are taking care of your customers and, on the other. In this way, you can enhance and bring further delight to their experience with your brand measurement.
Excellent products, a praiseworthy website, and an on-call customer service team may seem like the perfect mix to capture prospective clients. However, when customers feel something is off in your communication, they’re more likely to seek competitors.
By improving the customer experience at each touchpoint in the customer journey, you focus your business on your customers, putting them at the heart of all. This builds a loyal fan base and keeps customers coming back time and again, creating a strong connection throughout the entire customer journey. This builds brand loyalty as a positive outcome, leading to having satisfied customers and an influence over their lives, choosing your brand above others.
The brands that gain the most loyalty are the ones that influence their clients’ lives. It is the outcome of so many variables —some of which we can control and others we cannot—and understanding how those variables play out in our markets is a crucial first step to understanding what causes brand loyalty.
If you like reading about the customer journey, you might find it interesting to learn about the difference between Customer Journey vs Customer Experience.
Customer Journey Stages
Now that you know what a customer journey is, it’s time to look more closely at what you can do to commit to your present and potential clients. Various stages make up the complete journey.
These three steps generally make up most journeys: Awareness, Consideration, and Conversion. These customer journey stages are most suitable for offline purchases.
With the progress of digital platforms, two critical additions appear in the customer experience: Retention and Advocacy. These new stages of the customer journey explore brand touchpoints with online shoppers.
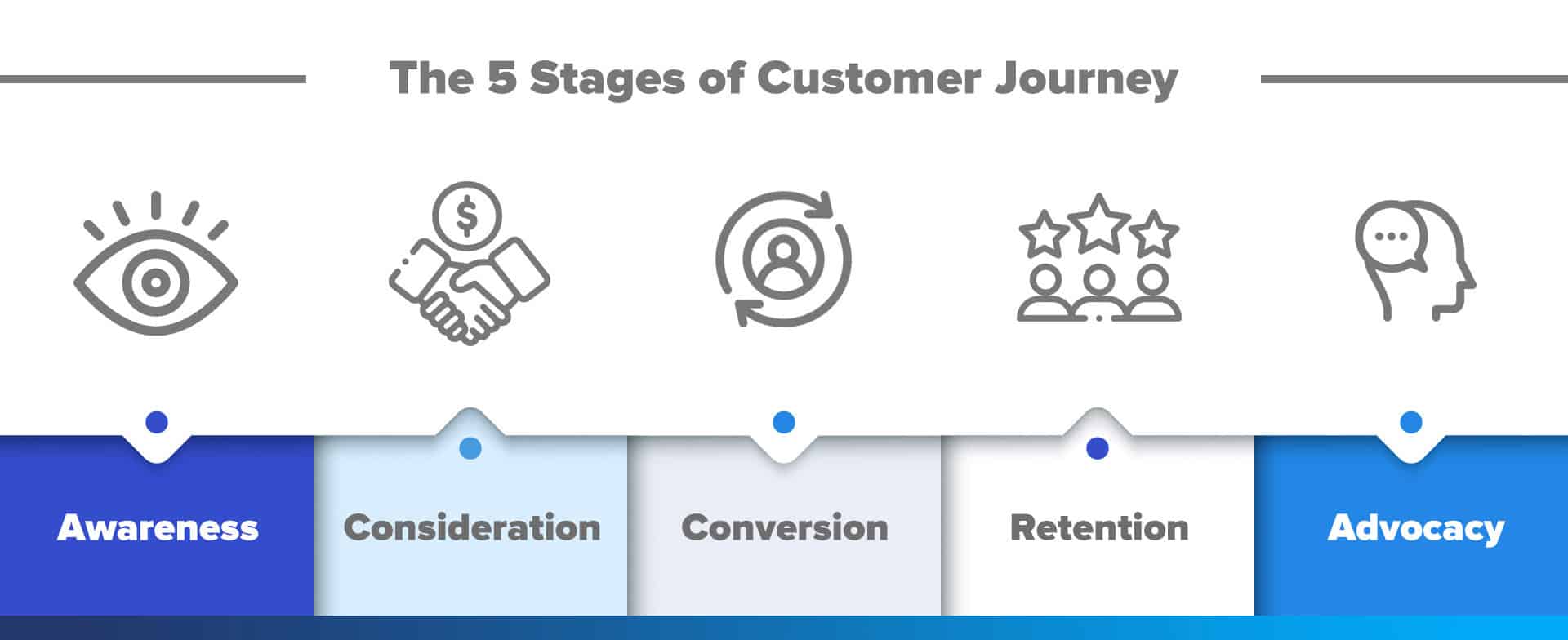
1. Awareness: The first stage
Awareness involves spreading general information about your products and services to your target audience(s).
During the customer awareness stage of the customer journey, consumers search for solutions and encounter multiple brands and products. Hint: This is the time to shine if you want to make a good first impression.
What consumers are doing: During this customer journey step, consumers are likely conducting research. This can include searching online for solutions to keyword problems, reading blog posts and news articles, browsing online forums, and first meeting brands.
What brands can do: You might think consumers are doing all the heavy lifting at this stage of the customer journey because they’re asking questions and browsing content.
However, you don’t want to approach brand awareness passively. You have to be there already, where the consumer is looking at alternatives. By “being there,” we mean taking the form of an educational blog post or video, providing the solution or information they want. Bringing valuable resources to the consumer is vital in this initial customer journey phase.
2. Consideration: The second stage
Brands focus on promotion during the consideration stage of the customer journey. This is where customers begin to look for alternatives to past purchases. During this journey phase, your business strives to convince potential buyers to include you on the list of available options.
Your brand will most likely be considered alongside others, so make sure every impression you make counts.
At this point, consumers are directly interacting with your brand, and you want them to stick around for the next step in the customer journey.
What consumers do: Research specific brands and products, compare competitors, and evaluate your priorities. This could include looking closely at your product and service specifications and features, examining customer support policies, and turning to direct comparison reviews.
The consideration phase of the journey varies because consumer-centric channels can come in many forms.
What brands can do: Value the importance of the user experience (UX). Continuously optimize the UX across all your touchpoints, including e-commerce transaction and description pages.
Little things like making sure the descriptions and processes are clear and that all the buttons work correctly go a long way when someone considers you against a competitor on their customer journey.
For instance, a person becomes aware they’re hungry and could be scouting for a place to eat on an app like Google Maps.
Suppose your business has a strong presence there, i.e., with information about what kind of food you sell, the menu, photos of the place and the food, phone number, and truthful, positive customer reviews. In that case, you might make them consider that you could be an excellent alternative to what they’re looking for.
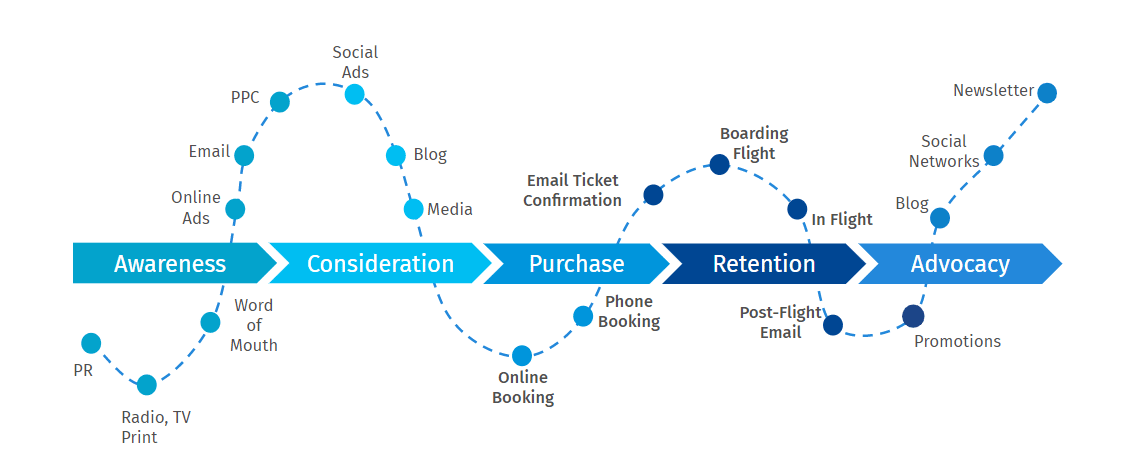
3. Conversion: The third stage
This stage of the customer journey prompts visitors to take a particular action. Using a dedicated call-to-action (CTA), you encourage customers to make a purchase, subscribe to a mailing list, or sign up for services. You should use this phase to sell your product as the best fit to solve a visitor’s problem.
It is your moment to make or break during the Customer Journey. Once potential customers are satisfied with researching and comparing their options, they will eventually decide.
Sometimes, they find that none of the brands they’ve been considering offer what they’re looking for. If they make a favorable decision, they want to make the process easier by choosing their trusted products.
What consumers are doing: They are considering factors like price vs. value, customer service responsiveness, company values, and policies as part of the existing customer journey. When they’re in the decision phase, it’s not just about product specifications or the shopping experience but how these elements fit into their customer journey design.
Consumers want to support a brand they trust to provide a quality solution to their problems, ensuring a positive customer journey begins and continues throughout their interaction with the company.
What brands can do: To anticipate this customer journey step, you must go further. This could include marketing strategies where you offer incentives to potential customers who have already visited your website or engaged with your business.
Ensure your return and refund policies are easy to find and train your customer support team to answer key decision-making questions.
Note that the following two customer journey stages, Retention and advocacy, were optional in previous business models. Nevertheless, the increase in online purchases makes these stages of the customer journey as significant as the others.
Read about the customer value journey and what it is.
4. Retention: The fourth stage
At this point in the customer journey, you already have a new customer – Congratulations! All that planning and asset building is paying off when they get to this phase. The journey refers to the consumer’s path from initial awareness to making a purchase, and in this phase, they have decided to navigate their purchase journey with you. But don’t assume it’s a done deal.
A loyal customer brings an organization consistent business and costs less than the effort to bring in new customers. A study by Bain & Company discovered that loyal customers are 50% more likely to try new products and spend 31% more than new customers. This demonstrates the value of nurturing and maintaining relationships with customers throughout their customer journey.
Retention includes keeping customers happy with a relationship management/customer success team to stop them from leaving and take them as many as possible to the next and final stage of the customer journey- make them so loyal to your brand that they want to advocate for your product and service.
What consumers are doing: Depending on your business model, customers are taking advantage of this moment to buy your products online, with a physical retailer, or are booking a service they plan to experience soon.
Once they have the product or service as a part of their consumer journey, they will start to implement their purchase, and if they go through the phase successfully, you will earn their customer loyalty.
What brands can do: Optimize the transaction experience in the Journey. Ensure the quality of your e-commerce site or physical store, and regularly review how your competition optimizes customers’ experience for each customer touchpoint.
5. Advocacy: The fifth stage of customer journey
Most organizations acknowledge the benefits of word-of-mouth. However, few companies commit to a plan for boosting customer advocacy. Encouraging each customer to share reviews can take time and money. Reaching out to influencers or guest bloggers is an effective alternative to traditional word-of-mouth.
Enthusiastic customers are more likely to recommend your brand and products to a friend, which can be a deal-breaker for many as it enhances the entire customer journey.
When you keep your customers happy and exceed their expectations with innovation and excellent customer service, the customer journey shortens, and transaction costs decrease.
What consumers are doing: At this point in the customer journey, customers are using your offerings to address their needs. The better the results and experience they get with your product, the more likely they will buy again and recommend you.
They can also begin to engage with your brand more casually on social media and plan their next purchase.
What brands can do: Take the initiative to contact customers in a friendly and supportive manner during their journey. A short customer experience survey is an excellent way to let them know you care about their feedback.
Consider starting a loyalty program for referrals and future transactions. This is also an excellent opportunity to keep consumers returning to some relevant assets you create to build brand awareness.
This could include blog content with tips to enrich your product experience, a newsletter with updates, promotions, and occasional opportunities to provide further feedback.
Are you thinking about improving your understanding of your customers? Dive into QuestionPro’s latest blog on their Customer Insight Platform!
Benefits of Understanding the Customer Journey
Identifying customer journeys allows us to better understand how they buy to meet their needs and expectations and what role a specific business plays in this process.
Furthermore, being aware of all their journey interactions (customer touchpoints) through any channel, such as email or social networks, allows for a better shopping experience while delivering a consistent message across all communication channels.
Next, we will explain the benefits of implementing a customer journey strategy in your business.
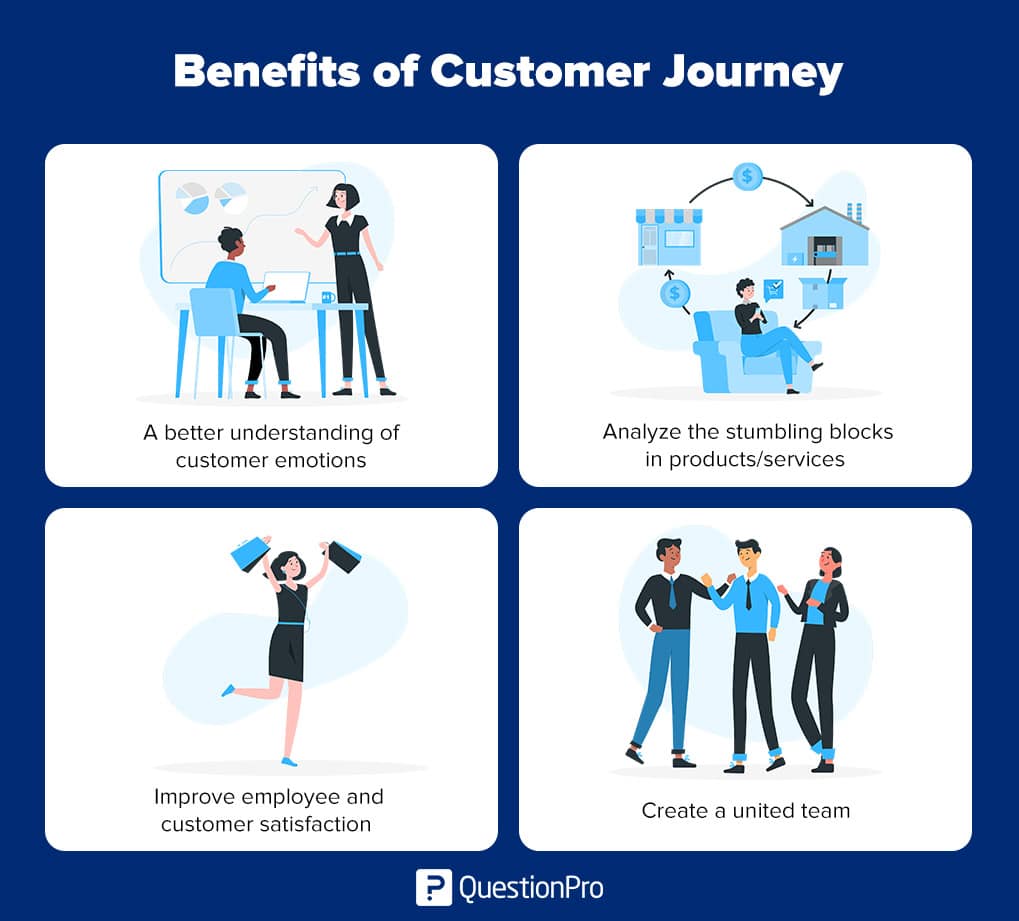
01. A better understanding of customer emotions
Building a customer journey framework puts you directly in the mind of the consumer. Understanding why a customer makes a particular choice sets your business up for success.
Knowing how customers feel encourages you to improve how the organization functions because it allows you to identify the friction points throughout their customer journey, making them easier to fix.
02. Analyze the stumbling blocks in products/services
Mapping the journey gives your organization insights into where your customer communications fall short. For instance, if your support staff is undermanned, customers don’t receive help when needed. Your customers become angry because they expect prompt replies. You resolve the issue by hiring another support team member to tackle more customer questions.
Creating a customer journey map provides the customer’s viewpoint of a business. The map is a visual representation of the transactions and emotions that lead through each touchpoint with customers, which helps to identify weak points in your messaging.
03. Improve employee and customer satisfaction
As issues are resolved, confidence levels among customers and employees alike increase, leading to a more positive customer journey. Employees are encouraged to continue doing great work, increasing overall customer satisfaction.
04. Create a united team
To develop unique customer experiences, the teams in your organization need to be on the same page. Marketing, product development, sales, and customer service must work together to improve customer journey processes within the organization. As the teams work together, the efficiency and effectiveness of each team increase, positively impacting the customer journey mapping process.
Make sure to check these 10 customer journey benefits for mapping
Customer Journey Analysis
Understanding the organization from the customer’s point of view brings new ideas and opinions to the table. Customer Journey Analytics does precisely that – it analyzes customer viewpoints about products so that you can make appropriate changes to keep customers loyal to your brand. Use data from customers to implement improved marketing strategies.
The analysis involves three stages: gathering accurate information, developing customer personas, and analyzing customer interactions.
Here is how customer journey analysis is beneficial in gathering information:
- Clearly defines all customer interaction points.
- Evaluates how the customer journey progresses from beginning to end.
- Analyzes the impact on customer loyalty and brand shareability according to customer interaction points.
- Highlights areas that waste a customer’s time to improve efficiency.
- Generalize the customer journey of similar audiences to make improvements and keep customers satisfied.
Learn what Customer Journey Monitoring is and the benefits of implementing this systematic activity.
Customer Journey Communication Channels
Your map is a 360-degree view of customer feedback from each step in their journey. Customer journey mapping is a proven model for understanding how, when, and where your customers experience your brand.
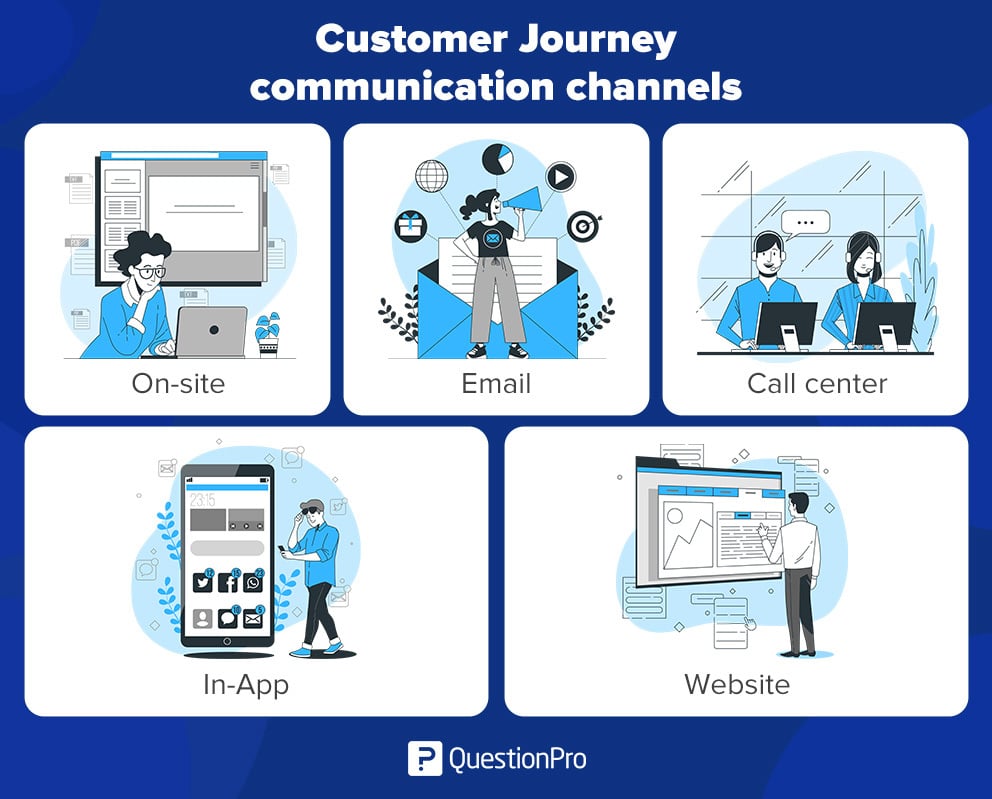
To start, here are some places to measure experience on an ongoing basis:
- On-site: Capture feedback at the moment customers visit businesses with physical locations. For example, let’s say you run a restaurant. Give diners a short survey to complete along with their bill at the end of their meal, allowing you to gather valuable insights into their customer journey.
- Email: Sending emails is one of the easiest ways to get customer feedback. Set up your sales system to trigger an email after a customer completes a purchase.
- Call center: After every customer interaction, you can collect feedback via email or phone-based survey.
- In-App: For app developers, collecting responses without leaving the app is ideal. An in-app survey allows users to continue enjoying the app while still providing you with feedback, contributing to a seamless customer journey.
- Website: Your prospects browse your site to consider becoming customers. Once customers continue visiting for support and account access, gathering feedback on your website is essential to a holistic customer experience approach.
If you like reading about what the customer journey is, you might find it interesting to learn about the in-store customer journey: definition, importance and stages.
Elements of the Customer Journey
There are various elements that are essential when creating your Customer Journey and that will help you have a better customer analysis.
Each of these elements will help you identify the points that you should improve on your journey:
1. Buyer persona
Buyer personas are iconic representations of your ideal customer. They are based on research, data, facts, and real interviews with recent buyers (and may even include perspectives from people who postponed a purchasing decision or purchased a competitive solution).
By creating a buyer persona correctly, marketing managers will be able to segment their messages better, targeting different people with the most appropriate content and offers; develop new products/services based on the needs and wants of its key customers; and reach the right people, thus pre-qualifying potential customers by attracting them.
Let’s remember that the journey of a customer is the story of a customer’s experience, and it helps you explain what happens along the way, to whom, and how it happens. Therefore, it is necessary to know who makes the trip to tell the story. The buyer persona represents the customers whose journey you are mapping.
2. Contact points or touchpoints
Where are the customer contact points? Touchpoints encompass all interactions between a brand and a customer at any point in the customer journey.
These individual touchpoints can influence how a customer perceives your overall brand experience. Every touchpoint represents an opportunity to guide and delight the customer.
Touchpoints can occur through web and offline channels and may or may not be controlled by the brand.
These are some channels you can use to stay in touch during the journey:
- Website
- In the place
- Via telephone
- Social networks
- Word-of-mouth recommendations
- Apps
- Evaluation sites
- SMS
The number of customer touchpoints and the time it takes to complete each step can vary depending on multiple factors, including:
- Customer preferences (i.e., preferred mode of searching, purchasing, support, etc.).
- Relevance and importance of the goal (for example, buying a car compared to buying food for your dog)
- The channels are chosen by companies to interact with their customers.
3. Performance indicators
A key role is to identify critical opportunity areas based on understanding your customers’ perceptions of the experiences.
You can use common indicators that indicate positive/neutral/negative or exceeds/meets/does not meet expectations. This generalized approach to performance indicators can be used effectively to identify and evaluate areas of opportunity.
Because qualitative research is typically conducted with smaller sample sizes, quantitative research with a large sample size can strengthen confidence in qualitative insights.
Quantitative research provides an opportunity to capture customer experience metrics for specific journey stages or touchpoints. By integrating metrics into the customer journey map, they become a useful tool for measuring customer experience initiatives over time. Some useful metrics you can include are:
- Net Promoter Score (NPS) or other customer loyalty measures
- Customer satisfaction metrics
- Quantitative assessments of the primary emotions customers are experiencing at specific stages or touchpoints in their journey
- Effort metrics
- Measures of importance, usefulness, etc. from a specific point of contact
The metrics collected and included in the Customer Journey will help you measure the health of the customer experience, now and in the future. And in doing so, there must be a commitment to making value decisions based on customer experience performance.
4. Customer experience map
The customer experience map helps you list the following elements that will help satisfy users and compel them to move forward. Consider these examples:
- Consumer activities and questions
- Touchpoints such as websites, forums, and advertisements
- Assets such as paid media, blog posts, videos, and webinars (some assets are customer touchpoints)
- Strategies such as SEO, social networks, managing virtual communities, and creating referral programs
- Tools like engagement reports and online surveys.
How to Define a Customer Journey Effectively?
After learning what a Customer Journey is and the elements that make it up, it is time to build a journey map that converts prospects into loyal customers and creates the best strategy.
Follow these 5 steps to ensure your customers get the products they need for their needs and enjoy a customer experience that will keep them coming back to your business.
1- Understand what you have to offer and who benefits from it
Each member of your team should know how to communicate the benefits of your products and services. You can’t share something when you don’t know what it is! In the same way, you need to know who your ideal client is.
Ask yourself, “Who needs this solution most?” This is a good opportunity to take advantage of online surveys, which allow you to identify your target audience, their primary needs related to your offers, and any other considerations you need to make to attract them.
2- Create your ideal client
Once you have a general idea of who your target audience is, create a few profiles to give them a name and a face. When you have a well-developed sense of who to include in your demographic segmentation, you’ll have a clear understanding of the variations in your customers’ journeys.
For example, you may discover that your reusable water bottles will solve problems for athletes of all ages, sustainability-conscious millennials, and adults with limited mobility. Avoid expanding your market too much because that can blur your focus and make your market strategies less efficient.
Create a customer archetype for each of these groups within your target audience, taking into account these imaginary but realistic variables:
- Gender
- Age
- Economic situation/income range
- Occupation
- Interests and hobbies
- Main sources to communicate and obtain information
- Habits
- Consistent touchpoints
- Favorite brands and products
- Consumption habits
3- Identify any specific details of your industry
The next strategy to create an effective Customer Journey is to obtain details of your industry.
Generally, customers’ stops along their journey will be similar. However, their specific needs should influence your value propositions and the assets you create to market your product.
4- Optimize your value propositions
The Customer Journey is personal, and your value propositions must be consistent in each encounter with consumers.
As you become familiar with your target market, refine your value propositions to be inclusive, communicative, and aspirational. Use these statements as a guide in your customer journey map and your company’s marketing assets.
It’s time to put your customer experience map into practice. Consider what each of your customers would need and do so throughout the entire process while assigning these elements to each phase of the customer journey map.
5- Build assets for each touchpoint in the Customer Journey
By mapping out the customer journey, you’ll have a clearer idea of what your ideal consumers will ask of you, the brands they might be considering, and the types of content they’re likely to consume to move from one phase to the next.
Depending on your industry, customer touchpoint content may include the following asset types:
- Blog posts
- Associated or influential content
- Print or email newsletters
- Infographics
- Information on social networks
- Surveys
- Videos (ads, tutorials, webinars)
- Promotional flyers
- Sample kits or demos
What is Customer Journey Mapping?
A Customer Journey Map (CJM) tells the story of your customer’s experiences with your brand across every touchpoint – all on the same canvas. Or Customer Journey Map (CJM) as a key tool to improve the customer experience. Depending on the objective of the CJM, it can be more or less complex.
The things your customer feels, sees, and hears as they interact with your business, builds the foundation for their experience.
Understanding these experiences allows you to map and control the customer journey accurately.
Example of Customer Journey Mapping
Starbucks, for example, masters the concept of customer intimacy and uses customer journey maps to control the experience. The customer journey is calculated from the moment you step in the door.
Imagine a trip to your local Starbucks. As you walk inside, you smell the aroma of roasted coffee beans. The barista behind the counter greets you with a smile. As the muffled chit-chat disappears into the tranquil background music, you feel the coziness around you.
When you receive your coffee, you see your name handwritten by one of the friendly baristas, a personalized moment clearly indicated on the customer journey map. If you’re a regular, the staff knows you by name and can make your order from memory.
The coffee giant doesn’t just sell a product. It sells what people are best at remembering – the experience. The company retains loyal customers by packaging the product with an unforgettable experience. They’re also able to charge up to 10 times more than their competitors. Starbucks clearly understands customer experience and infuses that into the core of its business strategy.
Learn More: Click here if you’d like to review 7 more Customer Journey Examples.
Below, you will find a customer journey map template in case you need a reference to create your own. If you’d like to download the customer journey map template, keep reading! Or scroll down a little bit more 😉
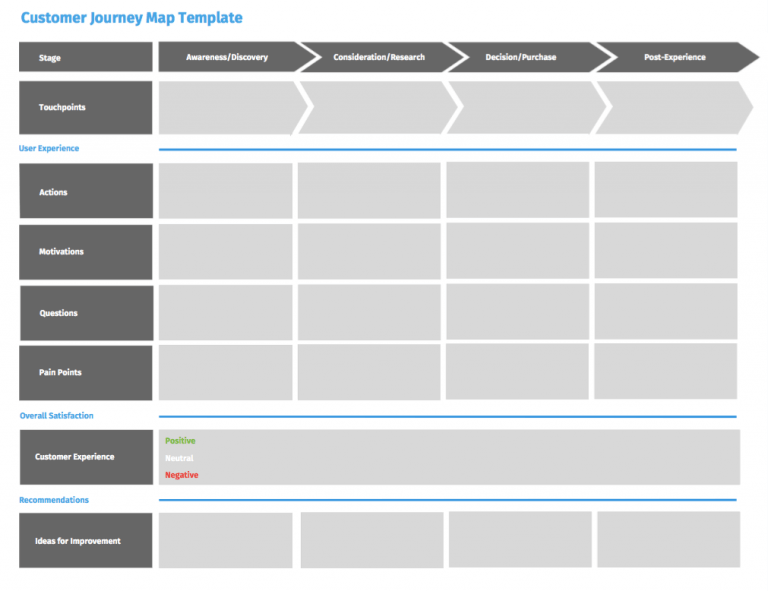
Your customer journey could take place over a few hours or more than several weeks. The simplest way to start is to create a timeline. Using your customer knowledge, fill in what’s happening with your customer at each stage of your customer journey timeline.
The customer journey mapping framework includes the following alongside the timeline:
- Actions: What is your customer doing? What are the key actions a customer takes to move to the next customer journey stage? What actions does a person take when they don’t move on?
- Motivations: What drives the customer to proceed to the next stage of the customer journey? What is the goal? Are they trying to solve a problem? What are they feeling?
- Questions: What are the customer’s uncertainties? Are they looking for something specific? Are they confused? Identify which stage of the journey customers have the most questions and quickly address them.
- Pain points: What obstacles prevent your customers from moving to the next stage? Is it the process? Price?
Direct customer opinions are the most effective way to get answers. Send surveys or conduct interviews to learn more about your customers and their needs. Input the data you receive into the framework above so you can see your company from your customer’s perspective.
Free eBook: The Hacker’s Guide to Customer Experience – CX= Emotion x Value
Halfway there? Congratulations! Luckily, you’ve learned a bit more about what Customer Journey is and its interconnection with customer experience. If you’d like to go the extra mile and learn more about how customer experience can help you gain happier, loyal customers and increase your business growth, download our free eBook: The Hacker’s Guide to Customer Experience – CX= Emotion x Value.
Tips for Conducting a Customer Journey Mapping
If you’ve made it this far, you would probably agree that knowing your customer’s journey is critical to creating a great customer experience. But how do you make the most out of it?
Let’s take a look at some of the following tips to create an effective Customer Journey Map:
Tip #1: Building a customer journey map is a team effort
It is not easy to reflect on the Customer Journey Map of all the interactions a customer goes through. The task can be further complicated when the people responsible for interaction cannot be found in the different departments.
This takes for granted the phases or interactions the client goes through with the company. What’s worse, it sometimes leads to mapping a Customer Journey Map that has more emphasis on departmental silos than the overall customer journey.
Remember, your team cannot forget the goal. It seeks to map the Customer Experience from its perspective. This is most effectively achieved when different company profiles are brought together. Only in this way will the final result reflect the knowledge that each one has of the client.
The idea is to dedicate a workspace with the different professionals, with and without client contact. If this is impossible, performing at least one validation with each department is vital. This will allow you to turn your Customer Journey Map into a shared responsibility tool.
Tip #2: Know your customer thoroughly
Understanding your customers at each intersection or checkpoint in their customer journey is critical. This allows you to develop content, products, and services that meet their needs. Rather than gathering occasional data from customers, employ continuous surveys to collect information.
You’ll enjoy the ability to adjust your marketing or product development in real-time to meet customer needs as the market changes.
Tip #3: Obtain a comprehensive view
The customer journey starts before potential customers purchase or sign up for services. Prospects begin their customer journey as they learn about offerings on your website, online review sites, or advertisements. After the awareness and discovery stages of the customer journey, consumers enter the purchase process. Customers experience your products and services when making a purchase and then form opinions.
Throughout these stages of the customer journey, you must know how customers feel about your business and products. For example, do you know what factors cause customers to choose you over the competition? How do customers perceive your sales staff? What do customers like about your products? Is your support team answering customer questions with accuracy?
How to Create a Customer Journey Map?
There are six main steps to creating a customer journey map:
Step 01: Understand the target buyer’s persona: An organization must define its ideal buyer’s persona before journey mapping.
Step 02: Acknowledge the target audience’s intent: What does a buyer hope to achieve by interacting with a brand? What are their expectations?
Answer these questions by:
- Sending out online surveys to all the customers
- Organizing focus groups or one-on-one interviews
Then, develop action plans using the results of your research to meet buyer expectations.
Step 03: Note the touchpoints: Map all interaction touchpoints every time new customers visit your website or contact a sales team member. Include interactions before, during, and after purchase in your customer journey map.
Your organization should understand:
- Where customers obtain information about your website – Google search, social media, or Google ads.
- Which pages do most customers visit? What’s the average time spent on each?
- Did the customers enjoy shopping with the organization? Did they face any difficulties, and how helpful was the customer service team?
Step 04: Ask crucial questions: It’s essential to ask questions such as:
- Does my organization satisfy all the requirements of my target audience?
- In which stages of the customer journey do customers face common problems?
- Which website pages have higher bounce rates than what is acceptable?
If you interact directly with customers, be sure to ask them:
- How did you know about our organization?
- What were your expectations from our organization’s website?
- Were your expectations satisfied?
- What prompted you to purchase from our organization?
Step 05: Make a list of priorities: You can optimize customer journey mapping by identifying the areas that need immediate attention. Once you know common problems, you can take steps to limit their impact on customer loyalty.
Step 06: Put all ideas to paper: Most marketers prefer drawing the entire map on a whiteboard or using customer journey mapping tools to create a digital customer journey. Refer to your copy when you need to make decisions to improve customer experience.
Learn: What is the buyer’s journey, and what is its difference from the customer journey?
Free Customer Journey Map Template
At QuestionPro, we know that all this information can be overwhelming, and starting to create your Customer Journey without help can be intimidating.
That is why we have created a Customer Journey Map Template that we hope can help you start sketching the stages, UX, and overall satisfaction of your customers with your brand.
or
DOWNLOAD CUSTOMER JOURNEY MAP TEMPLATE (PDF)
How to Use Customer Journey to Improve Your Customer Experience?
Customers expect every exchange with a brand to be seamless from the start. Understanding the interactions at each customer journey touchpoint helps you satisfy customer needs and improve your business’s efficiency.
“Customer-centric companies are 60% more profitable than those not focused on the customer.” – Deloitte and Touche
To accurately map the customer journey, consider each stage of buying a product. At each customer journey stage, write down what a customer feels and the actions they must take to move forward.
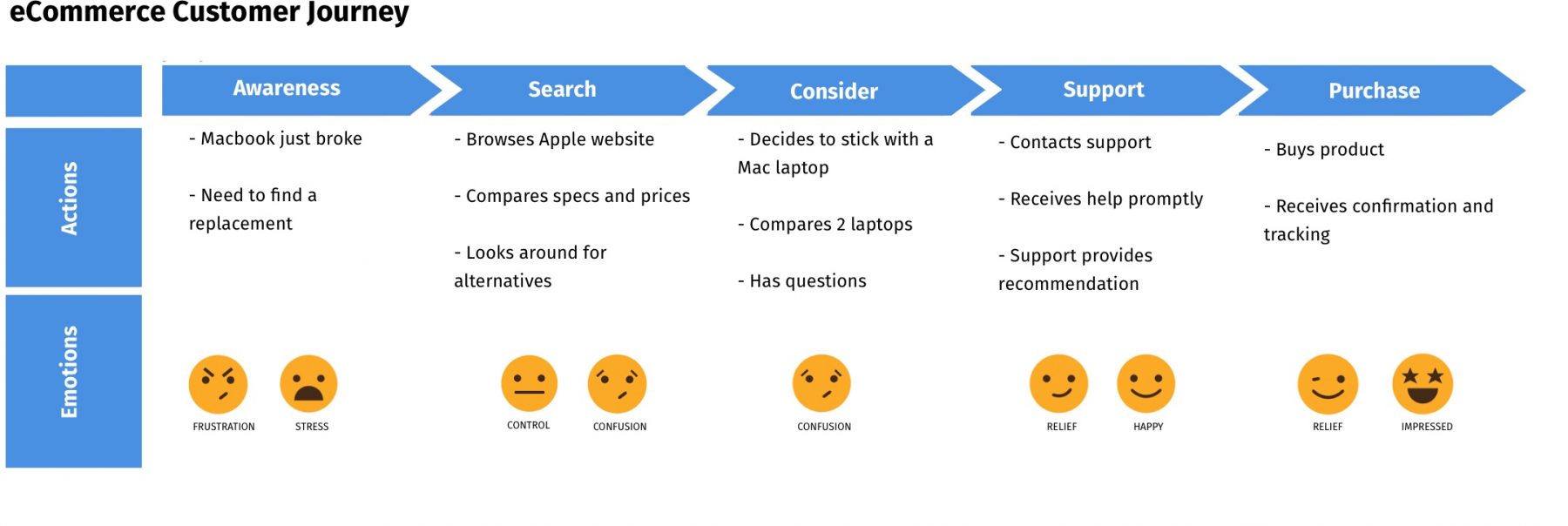
Examine the emotions at each touchpoint and rate the experiences. Is it positive or negative?
Begin to connect the dots and identify which gaps are falling short of your customer’s expectations. This exercise will help you formulate and decipher where you can have the most significant impact on improving the experience.
Learn more about the Customer Journey Canvas
Collect customer satisfaction feedback for more accurate results
Include your customer satisfaction scores as you map out your customer journey template. This additional information helps validate gaps or assumptions you make from mapping.
For example, your customer rates a CSAT score of 3 at their point of purchase and gives a score of 8 post-purchase. You immediately know that your point of sale requires attention.
Look at multiple customer satisfaction scores to find the most crucial pain points. If there is a customer journey touchpoint that ranks poorly for most customers, start your improvements there.
Learn about SaaS Customer Journey
Conclusion
The customer journey plays an important part in understanding and enhancing the customer experience. Businesses can identify necessary touchpoints, anticipate customer needs, and create stronger relationships by mapping out each stage- from awareness to post-purchase engagement.
Start following your customer’s journey and create a detailed customer journey map. QuestionPro offers some of the most advanced customer experience tools available. Gain valuable insights into your customers’ thoughts and emotions using QuestionPro CX today.







