In the world of research, there are two main types of data sources: primary and secondary. While primary research involves collecting new data directly from individuals or sources, secondary research involves analyzing existing data already collected by someone else. Today we’ll discuss secondary research.
One common source of this research is published research reports and other documents. These materials can often be found in public libraries, on websites, or even as data extracted from previously conducted surveys. In addition, many government and non-government agencies maintain extensive data repositories that can be accessed for research purposes.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
While secondary research may not offer the same level of control as primary research, it can be a highly valuable tool for gaining insights and identifying trends. Researchers can save time and resources by leveraging existing data sources while still uncovering important information.
What is Secondary Research: Definition
Secondary research is a research method that involves using already existing data. Existing data is summarized and collated to increase the overall effectiveness of the research.
One of the key advantages of secondary research is that it allows us to gain insights and draw conclusions without having to collect new data ourselves. This can save time and resources and also allow us to build upon existing knowledge and expertise.
When conducting secondary research, it’s important to be thorough and thoughtful in our approach. This means carefully selecting the sources and ensuring that the data we’re analyzing is reliable and relevant to the research question. It also means being critical and analytical in the analysis and recognizing any potential biases or limitations in the data.
LEARN ABOUT: Level of Analysis
Secondary research is much more cost-effective than primary research, as it uses already existing data, unlike primary research, where data is collected firsthand by organizations or businesses or they can employ a third party to collect data on their behalf.
LEARN ABOUT: Data Analytics Projects
Secondary Research Methods with Examples
Secondary research is cost-effective, one of the reasons it is a popular choice among many businesses and organizations. Not every organization is able to pay a huge sum of money to conduct research and gather data. So, rightly secondary research is also termed “desk research”, as data can be retrieved from sitting behind a desk.
The following are popularly used secondary research methods and examples:
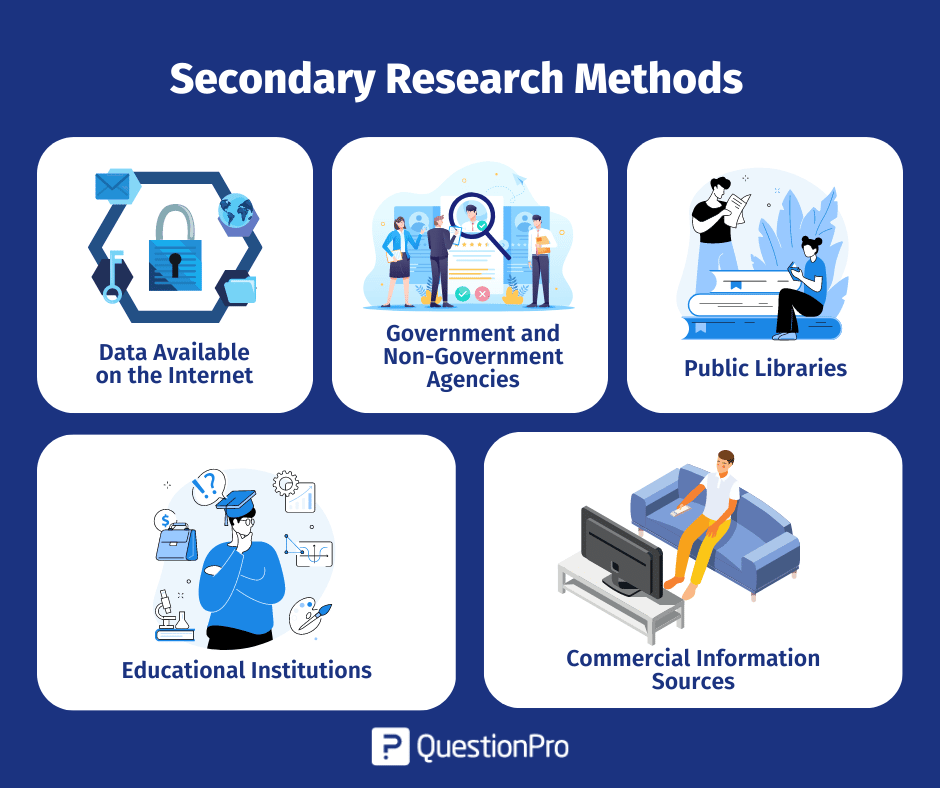
1. Data Available on The Internet
One of the most popular ways to collect secondary data is the internet. Data is readily available on the internet and can be downloaded at the click of a button.
This data is practically free of cost, or one may have to pay a negligible amount to download the already existing data. Websites have a lot of information that businesses or organizations can use to suit their research needs. However, organizations need to consider only authentic and trusted website to collect information.
2. Government and Non-Government Agencies
Data for secondary research can also be collected from some government and non-government agencies. For example, US Government Printing Office, US Census Bureau, and Small Business Development Centers have valuable and relevant data that businesses or organizations can use.
There is a certain cost applicable to download or use data available with these agencies. Data obtained from these agencies are authentic and trustworthy.
3. Public Libraries
Public libraries are another good source to search for data for this research. Public libraries have copies of important research that were conducted earlier. They are a storehouse of important information and documents from which information can be extracted.
The services provided in these public libraries vary from one library to another. More often, libraries have a huge collection of government publications with market statistics, large collection of business directories and newsletters.
4. Educational Institutions
Importance of collecting data from educational institutions for secondary research is often overlooked. However, more research is conducted in colleges and universities than any other business sector.
The data that is collected by universities is mainly for primary research. However, businesses or organizations can approach educational institutions and request for data from them.
5. Commercial Information Sources
Local newspapers, journals, magazines, radio and TV stations are a great source to obtain data for secondary research. These commercial information sources have first-hand information on economic developments, political agenda, market research, demographic segmentation and similar subjects.
Businesses or organizations can request to obtain data that is most relevant to their study. Businesses not only have the opportunity to identify their prospective clients but can also know about the avenues to promote their products or services through these sources as they have a wider reach.
Learn More: Data Collection Methods: Types & Examples
Key Differences between Primary Research and Secondary Research
Understanding the distinction between primary research and secondary research is essential in determining which research method is best for your project. These are the two main types of research methods, each with advantages and disadvantages. In this section, we will explore the critical differences between the two and when it is appropriate to use them.
| Primary Research | Secondary Research |
| Research is conducted first hand to obtain data. Researcher “owns” the data collected. | Research is based on data collected from previous researches. |
| Primary research is based on raw data. | Secondary research is based on tried and tested data which is previously analyzed and filtered. |
| The data collected fits the needs of a researcher, it is customized. Data is collected based on the absolute needs of organizations or businesses. | Data may or may not be according to the requirement of a researcher. |
| Researcher is deeply involved in research to collect data in primary research. | As opposed to primary research, secondary research is fast and easy. It aims at gaining a broader understanding of subject matter. |
| Primary research is an expensive process and consumes a lot of time to collect and analyze data. | Secondary research is a quick process as data is already available. Researcher should know where to explore to get most appropriate data. |
How to Conduct Secondary Research?
We have already learned about the differences between primary and secondary research. Now, let’s take a closer look at how to conduct it.
Secondary research is an important tool for gathering information already collected and analyzed by others. It can help us save time and money and allow us to gain insights into the subject we are researching. So, in this section, we will discuss some common methods and tips for conducting it effectively.
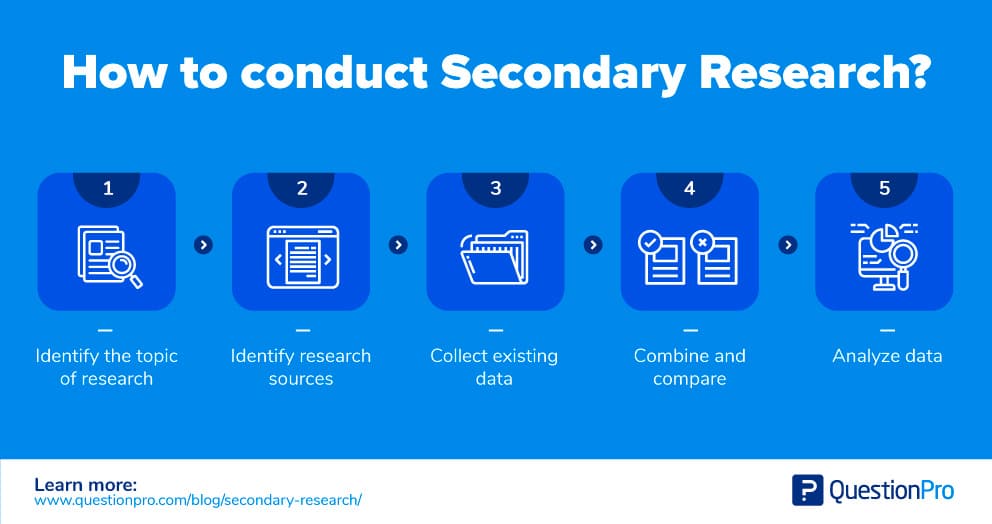
Here are the steps involved in conducting secondary research:
1. Identify the topic of research: Before beginning secondary research, identify the topic that needs research. Once that’s done, list down the research attributes and its purpose.
2. Identify research sources: Next, narrow down on the information sources that will provide most relevant data and information applicable to your research.
3. Collect existing data: Once the data collection sources are narrowed down, check for any previous data that is available which is closely related to the topic. Data related to research can be obtained from various sources like newspapers, public libraries, government and non-government agencies etc.
4. Combine and compare: Once data is collected, combine and compare the data for any duplication and assemble data into a usable format. Make sure to collect data from authentic sources. Incorrect data can hamper research severely.
4. Analyze data: Analyze collected data and identify if all questions are answered. If not, repeat the process if there is a need to dwell further into actionable insights.
Advantages of Secondary Research
Secondary research offers a number of advantages to researchers, including efficiency, the ability to build upon existing knowledge, and the ability to conduct research in situations where primary research may not be possible or ethical. By carefully selecting their sources and being thoughtful in their approach, researchers can leverage secondary research to drive impact and advance the field. Some key advantages are the following:
1. Most information in this research is readily available. There are many sources from which relevant data can be collected and used, unlike primary research, where data needs to collect from scratch.
2. This is a less expensive and less time-consuming process as data required is easily available and doesn’t cost much if extracted from authentic sources. A minimum expenditure is associated to obtain data.
3. The data that is collected through secondary research gives organizations or businesses an idea about the effectiveness of primary research. Hence, organizations or businesses can form a hypothesis and evaluate cost of conducting primary research.
4. Secondary research is quicker to conduct because of the availability of data. It can be completed within a few weeks depending on the objective of businesses or scale of data needed.
As we can see, this research is the process of analyzing data already collected by someone else, and it can offer a number of benefits to researchers.
Disadvantages of Secondary Research
On the other hand, we have some disadvantages that come with doing secondary research. Some of the most notorious are the following:
1. Although data is readily available, credibility evaluation must be performed to understand the authenticity of the information available.
2. Not all secondary data resources offer the latest reports and statistics. Even when the data is accurate, it may not be updated enough to accommodate recent timelines.
3. Secondary research derives its conclusion from collective primary research data. The success of your research will depend, to a greater extent, on the quality of research already conducted by primary research.
LEARN ABOUT: 12 Best Tools for Researchers
Conclusion
In conclusion, secondary research is an important tool for researchers exploring various topics. By leveraging existing data sources, researchers can save time and resources, build upon existing knowledge, and conduct research in situations where primary research may not be feasible.
There are a variety of methods and examples of secondary research, from analyzing public data sets to reviewing previously published research papers. As students and aspiring researchers, it’s important to understand the benefits and limitations of this research and to approach it thoughtfully and critically. By doing so, we can continue to advance our understanding of the world around us and contribute to meaningful research that positively impacts society.
QuestionPro can be a useful tool for conducting secondary research in a variety of ways. You can create online surveys that target a specific population, collecting data that can be analyzed to gain insights into consumer behavior, attitudes, and preferences; analyze existing data sets that you have obtained through other means or benchmark your organization against others in your industry or against industry standards. The software provides a range of benchmarking tools that can help you compare your performance on key metrics, such as customer satisfaction, with that of your peers.
Using QuestionPro thoughtfully and strategically allows you to gain valuable insights to inform decision-making and drive business success. Start today for free! No credit card is required.